User Ideas / Prospects
- Roles: Design and develop farming machinery, equipment, and tools; implement irrigation and drainage systems.
- Key Skills and Tools:
- Mechanical Design: Use of CAD software like AutoCAD, SolidWorks, and CATIA for designing machinery.
- Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulics: Understanding hydraulic systems and pumps for irrigation and drainage.
- Structural Engineering: Designing farm structures using tools like Revit for drafting and structural analysis.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Familiarity with environmental analysis tools like COMSOL Multiphysics.
- Roles: Design efficient irrigation systems, analyze soil and weather data, and manage water resources.
- Key Skills and Tools:
- GIS and Mapping Software: Use ArcGIS, QGIS, or AutoCAD Civil 3D for designing water distribution systems.
- Hydrology: Knowledge of hydrologic models and tools like HEC-RAS for flood and water flow simulation.
- Soil Moisture Sensors: Familiarity with installing and interpreting data from soil sensors (e.g., TDR and Capacitance Probes).
- Water Management: Knowledge of Evapotranspiration (ET) rates and irrigation scheduling software like CropManage.
- Roles: Implement precision farming technologies using GPS, sensors, and drones.
- Key Skills and Tools:
- GIS and Remote Sensing: Use ArcGIS, ENVI, and Erdas Imagine to analyze satellite imagery and map fields.
- Drones (UAVs): Operate drones for aerial surveys and analysis using software like DroneDeploy and Pix4D.
- Data Analytics: Analyzing farm data using Python, R, and MATLAB to optimize input use (e.g., fertilizers, water).
- GPS Technology: Understanding of GPS-enabled equipment for precision mapping of fields (e.g., Trimble and John Deere precision farming systems).
- Roles: Design, test, and maintain agricultural machinery such as tractors, harvesters, and irrigation systems.
- Key Skills and Tools:
- Mechanical Engineering: Use of SolidWorks, ANSYS, or AutoCAD to design and simulate machinery.
- Automation and Robotics: Knowledge of programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and industrial robotics (e.g., Siemens, Allen-Bradley).
- Machinery Maintenance: Diagnostics tools like CAT Electronic Technician (ET) and JDLink for real-time monitoring of machinery health.
- Energy Efficiency: Optimization using tools like MATLAB for improving fuel efficiency in equipment.
- Roles: Minimize environmental impact of farming practices, manage agricultural waste, and improve soil health.
- Key Skills and Tools:
- Sustainability Assessment Tools: Use of SimaPro or GaBi for lifecycle analysis and evaluating the environmental impact of farm practices.
- Waste Management Systems: Knowledge of designing manure and composting systems using AutoCAD and HydroCAD.
- Soil Conservation Technologies: Implementing tools like WEPP (Water Erosion Prediction Project) for soil erosion control.
- Renewable Energy: Working with solar and bioenergy systems, using PVSyst for solar energy simulation.
- Roles: Design food processing systems for packaging, storing, and preserving agricultural products.
- Key Skills and Tools:
- Process Automation: Use of PLCs and SCADA systems (e.g., Wonderware, LabVIEW) to automate food processing systems.
- Thermodynamics & Refrigeration: Design refrigeration and thermal processing systems using tools like AutoCAD MEP or SolidWorks Flow Simulation.
- Packaging Technology: Familiarity with Esko for packaging design and ArtiosCAD for structural packaging solutions.
- Quality Control: Use of Six Sigma methodologies and software like Minitab for process optimization.
- Roles: Design and implement strategies to manage water resources and prevent soil erosion.
- Key Skills and Tools:
- Soil Science: Use of soil analysis software like Hydrus to model water movement and retention in soil.
- Watershed Management: Familiarity with tools like SWAT (Soil and Water Assessment Tool) for modeling watersheds and analyzing land use impact on water flow.
- Erosion Control Technologies: Use of Civil 3D and HEC-HMS for designing drainage and erosion control structures.
- Land Restoration: Knowledge of reforestation, crop rotation planning, and the use of sustainable land management software.
- Roles: Implement cutting-edge technologies such as robotics, IoT, and AI to optimize farm operations.
- Key Skills and Tools:
- Robotics and Automation: Use of ROS (Robot Operating System) and programming in Python or C++ for automating agricultural tasks.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Implement IoT solutions using platforms like AWS IoT or Azure IoT Hub to monitor and manage farm equipment remotely.
- AI and Machine Learning: Build AI models using frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch for predictive analytics in crop management.
- Drone and Sensor Integration: Develop real-time monitoring systems with platforms like ThingSpeak or IBM Watson IoT.
- Roles: Develop systems to manage, store, and transport crops post-harvest.
- Key Skills and Tools:
- Refrigeration Systems: Design cold storage systems using Revit MEP or AutoCAD MEP to manage temperature and humidity.
- Supply Chain Management: Use of SAP or Oracle Supply Chain Management for optimizing logistics and distribution of perishable goods.
- Packaging Engineering: Develop sustainable packaging using tools like ArtiosCAD for 3D modeling and Esko Studio for visual packaging design.
- Quality Assurance: Implement quality control systems using HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) and tools like LabWare LIMS.
- Roles: Conduct research on new agricultural technologies and improve existing ones through trials and experimentation.
- Key Skills and Tools:
- Statistical Analysis: Use of SPSS, R, or SAS for analyzing experimental data and interpreting results.
- Lab Equipment and Experimentation: Operate farm research equipment, data loggers, and field sensors (e.g., LI-COR for environmental measurements).
- Experimental Design Tools: Use of software like Design-Expert or Minitab for designing and analyzing agricultural experiments.
- Collaboration Platforms: Share research findings using collaborative platforms such as Mendeley or EndNote for citation management.
This list highlights the specific tools and knowledge required for each role in agricultural engineering, ensuring that engineers are equipped with the right expertise to advance farming technology and sustainability.
The future of agricultural engineering is poised for significant transformation as it integrates more advanced technologies and adapts to global challenges such as climate change, resource scarcity, and population growth. Some key trends and technologies shaping the future of agricultural engineering include:
1. Precision Agriculture- Key Technologies: GPS, drones, and satellite imagery will continue to be integrated with farming equipment to precisely monitor crop conditions, soil moisture levels, and other critical factors. This approach allows for optimized input usage (water, fertilizers, pesticides) and higher crop yields.
- Impact: Precision agriculture can improve efficiency and sustainability by reducing waste and increasing productivity. With AI-powered analytics, farmers can make real-time decisions based on data.
- Future Prospects: The increasing affordability and accessibility of sensors and AI tools will make precision agriculture more widespread across both large-scale and smallholder farms
.
- Key Technologies: Autonomous tractors, harvesters, and weeding robots are becoming more common. These machines reduce labor costs and increase productivity, particularly in regions facing labor shortages.
- Impact: Automated equipment can work around the clock, which is especially important for time-sensitive farming operations such as planting and harvesting. Robots can also perform tasks such as weeding or fruit picking, which traditionally require manual labor.
- Future Prospects: As robots become more sophisticated, they will handle even more complex agricultural tasks, such as precision planting and selective harvesting.
- Key Technologies: Vertical farming uses LED lighting, hydroponic or aeroponic systems, and climate-controlled environments to grow crops in urban areas. CEA includes greenhouses and indoor farms that can produce food year-round, regardless of outdoor conditions.
- Impact: Vertical farms reduce land usage and transportation costs, while CEA systems can produce higher yields with fewer inputs. This is critical for feeding growing urban populations sustainably.
- Future Prospects: As urbanization increases, vertical farming could become a key solution to local food production. Innovations in LED technology, energy efficiency, and water recycling will make this approach more economically viable .
- Key Technologies: Sustainable agriculture involves using renewable energy (solar, wind), reducing water and fertilizer use, and implementing crop rotation and conservation tillage.
- Impact: These practices can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve soil health, and protect biodiversity.
- Future Prospects: Governments and global organizations are likely to promote policies supporting sustainable practices, with a strong focus on carbon-neutral farming .
- Key Technologies: Genetic modification (GM), CRISPR gene editing, and other biotechnologies will allow for the creation of crops that are more resistant to drought, pests, and diseases. This will be critical in adapting to the effects of climate change.
- Impact: These innovations could lead to higher crop yields, improved nutritional quality, and crops that require fewer inputs such as water and pesticides.
- Future Prospects: Biotechnology will continue to evolve, potentially allowing for even more precise manipulation of crop genomes to suit specific environmental conditions .
- Impact: Technologies like drought-resistant seeds and precision irrigation systems will allow farmers to continue growing crops in increasingly hostile environments.
- Future Prospects: Climate change is a major driver of innovation in agricultural engineering, and research will likely focus on ensuring that farming systems can withstand environmental stresses .
In conclusion, agricultural engineering has very bright future that heavily incorporates automation, data-driven farming, sustainability, and biotechnology. These advancements will allow farmers to produce more food with fewer resources, reduce environmental impact, and adapt to the growing challenges of climate change.
Notable Asian agricultural engineers, scientists, and innovators who have made remarkable contributions to agricultural development in Asia. Their work has improved food security, introduced new technologies, and empowered smallholder farmers, contributing to the transformation of agriculture across the continent.
Key Asian Agricultural Engineers, Scientists, and Innovators

- Contribution: Known as the "Father of Hybrid Rice," Yuan Longping developed the first high-yielding hybrid rice varieties, which significantly increased rice production and helped alleviate hunger in China and other Asian countries.
- Impact: His innovations in hybrid rice have been adopted worldwide, helping feed billions of people.
- Famous Quote: "To make a greater contribution to mankind, we should not only meet the needs of China but also help feed the world."

- Contribution: Known as the "Father of the Green Revolution" in India, Swaminathan introduced high-yielding varieties of wheat and rice that helped India achieve self-sufficiency in food production during the 1960s and 70s.
- Impact: His work prevented famines in India and significantly improved the country’s food security.
- Famous Quote: "If agriculture goes wrong, nothing else will have a chance to go right."
3. William Dar (1953–Present) – Philippines
- Contribution: Dar is a leading agricultural scientist and former Secretary of Agriculture in the Philippines. He has been instrumental in promoting sustainable farming practices and crop diversification in Asia.
- Impact: His work at the International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) has improved food security in drought-prone areas through innovations in crop production and soil management.
- Famous Quote: "Agriculture must be resilient, sustainable, and inclusive to tackle the challenges of climate change and food security."

- Contribution: An agricultural economist, Hossain was a champion of rural development and food security in Bangladesh. He worked at the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) and led efforts to improve rice productivity in Asia.
- Impact: His research helped increase rice yields, reduce hunger, and improve livelihoods for millions of farmers in Asia’s rice-growing regions.
- Famous Quote: "Agricultural research and innovation are the pillars of food security in Asia
5. Sayed Azam-Ali (1956–Present) – Malaysia: A leading researcher on underutilized crops and sustainable agriculture, Azam-Ali focuses on food crops that can improve nutrition and food security in developing nations.
Famous Quote: "We must broaden our food base to ensure food security in the face of climate change and population growth."
Continuing the LegacyThese Asian agricultural engineers, scientists, and innovators have made significant contributions to the development of sustainable agricultural practices, food security, and innovative technologies. Their efforts in biotechnology, soil management, precision farming, and water conservation have improved productivity, empowered smallholder farmers, and ensured the continent’s ability to meet the challenges of feeding a growing population in the face of climate change.
Note this list I did text without any particular order and best of my memory text me if you don't agree any of i mentioned or someone i Missed.
list of notable African agricultural engineers, scientists, and innovators whose contributions have been crucial in transforming the agricultural landscape of the continent, improving food security, and combating hunger. These individuals have introduced innovations and policies that have had a lasting impact on African agriculture, empowering farmers and ensuring sustainable development.
Key African Agricultural Engineers, Scientists, and Innovators1. Akinwumi Adesina (1960–Present) – Nigeria

- Contribution: As President of the African Development Bank and a former Nigerian Minister of Agriculture, Adesina played a crucial role in driving agricultural transformation across Africa, launching initiatives like the Alliance for a Green Revolution in Africa (AGRA).
- Impact: His efforts have promoted the use of modern farming techniques, fertilizers, and agricultural policies, significantly increasing food security across Africa. He received the World Food Prize in 2017.
- Famous Quote: "The future of Africa’s development depends on agriculture, and agriculture depends on youth."
- Contribution: An agricultural scientist and plant breeder, Ejeta developed drought-resistant and pest-resistant sorghum varieties, critical to ensuring food security in sub-Saharan Africa.
- Impact: His work has been instrumental in improving the productivity of sorghum, a staple food in Africa, and his innovations have benefitted millions of smallholder farmers. He was awarded the World Food Prize in 2009.
- Famous Quote: "Science is a powerful tool to defeat hunger and poverty, but it requires dedication and global cooperation."

- Contribution: A plant pathologist and biotech expert, Wambugu has been a key figure in promoting biotechnology in African agriculture, particularly for smallholder farmers. She led efforts to develop genetically modified (GM) crops that are disease-resistant and higher yielding.
- Impact: Her work has improved food security in Kenya and other parts of Africa by increasing crop resilience to diseases and pests, especially in staple crops like maize.
- Famous Quote: "Biotechnology is not just about science, it’s about feeding the hungry and improving livelihoods."

- Contribution: As former Secretary-General of the United Nations, Annan was a vocal advocate for agricultural development in Africa. He served as the Chairman of the Alliance for a Green Revolution in Africa (AGRA), promoting agricultural reforms and innovation.
- Impact: His leadership at AGRA was key in driving efforts to improve seed quality, agricultural productivity, and farmer support systems across the continent.
- Famous Quote: "The future of Africa’s development depends on transforming its agriculture."

- Contribution: Although born in Israel, Hillel's groundbreaking work in micro-irrigation techniques has had a lasting impact on African agriculture. His irrigation innovations helped regions facing water scarcity optimize water use for agricultural productivity.
- Impact: His techniques have been adopted in arid and semi-arid regions of Africa, contributing to food security in water-scarce environments.
- Famous Quote: "Water and land are the essential ingredients for the survival and prosperity of humanity."

- Contribution: Jones is an agricultural scientist known for developing the New Rice for Africa (NERICA) hybrid, which significantly boosts rice yields and is resistant to drought and disease.
- Impact: His work on rice breeding has improved rice production across Africa, enhancing food security and reducing dependence on imported rice.
- Famous Quote: "Agricultural transformation in Africa is possible with the right technology and the involvement of our farmers."
- Contribution: A renowned nutritionist and agricultural scientist, Oniang'o has worked tirelessly to improve food and nutrition security in Africa. She has been an advocate for women farmers and sustainable agricultural practices.
- Impact: Her research and advocacy have helped improve nutrition policies and practices, leading to healthier communities and more productive agricultural systems in Kenya and across Africa.
- Famous Quote: "The true wealth of a nation lies in the health of its people, which starts with the food they eat."

- Contribution: A prominent scientist and academic, Juma was a leading advocate for the use of science and technology to boost agricultural productivity in Africa. He promoted the use of biotechnology and agricultural innovations to tackle food insecurity.
- Impact: His work on agricultural policy and technological innovation has shaped global and African agricultural strategies, helping to advance the continent’s agricultural development.
- Famous Quote: "Innovation is the engine for growth in Africa’s agriculture."
- Contribution: Though Filipino by nationality, Dar’s work in Africa as Director General of the International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) has had a profound impact on African agriculture. He promoted agricultural research for dryland farming and crop improvement.
- Impact: His research on drought-resistant crops has improved agricultural productivity in semi-arid regions of Africa, helping millions of farmers adapt to climate change.
- Famous Quote: "Research is the key to unlocking the potential of African agriculture."
- Contribution: A former Rwandan Minister of Agriculture and President of AGRA, Kalibata has been a leading figure in advancing agricultural transformation across Africa, focusing on smallholder farmer support and sustainable farming practices.
- Impact: Under her leadership, AGRA has helped millions of African farmers increase their productivity and income through access to better seeds, technologies, and market systems.
- Famous Quote: "Agriculture is at the heart of Africa’s future, and we must invest in it for our people to thrive."

- Contribution: An agricultural scientist and soil expert, Bationo has worked extensively on improving soil fertility and sustainable farming practices in the Sahel region of Africa. His research focuses on soil health and nutrient management.
- Impact: His innovations in soil management have helped restore degraded soils and boost agricultural productivity in some of the most challenging environments in Africa.
- Famous Quote: "Healthy soils are the foundation of a thriving agricultural system."

Joseph DeVries (Present) – Kenya: Founder of the African Seed Access Index, DeVries has worked on improving access to high-quality seeds for smallholder farmers across Africa.
- Famous Quote: "Seeds are the foundation of agriculture, and access to quality seeds is the first step toward food security."
Kendi Mutungi (Present) – Kenya: An agricultural scientist focusing on post-harvest losses and food preservation, Mutungi advocates for improving storage and processing technologies to reduce food waste in Africa.
- Famous Quote: "Reducing post-harvest losses is crucial to ending hunger in Africa."
These African agricultural engineers and scientists have made remarkable contributions to their countries and the continent as a whole, ensuring better food security, productivity, and resilience. Their work in biotechnology, soil management, water conservation, and agricultural policy has provided lasting solutions to the food challenges Africa faces, bringing hope and prosperity to millions of people.
Note this list I did text without any particular order and best of my memory text me if you don't agree any of i mentioned or someone i Missed.
notable Indian agricultural engineers, scientists, and innovators whose contributions have been instrumental in shaping India’s agricultural sector, improving food security, and combating hunger. Their work has helped transform Indian agriculture into a more sustainable, productive, and resilient system.
Key Indian Agricultural Engineers and Innovators1.1. M. S. Swaminathan (1925–2023)

- Contribution: Father of India’s Green Revolution, Swaminathan introduced high-yielding wheat and rice varieties that helped India achieve self-sufficiency in food production during the 1960s and 70s.
- Impact: His efforts in agricultural research and policy saved millions from famine and significantly improved India’s food security.
- Famous Quote: "If agriculture goes wrong, nothing else will have a chance to go right."
- Contribution: Known as the "Father of the White Revolution" in India, Kurien was the architect of Operation Flood, the world’s largest dairy development program.
- Impact: His efforts made India the largest producer of milk in the world, improving rural incomes and nutritional standards.
- Famous Quote: "True development is not the development of land, or of cows; it is the development of men and women."

- Contribution: Known as the "Waterman of India," Singh pioneered water conservation techniques like rainwater harvesting and rejuvenation of rivers in drought-prone areas of Rajasthan.
- Impact: His work has improved water availability for agriculture, transforming barren lands into fertile fields and increasing food security in arid regions.
- Famous Quote: "The key to food security is water security."

- Contribution: A notable agricultural engineer and former director of the Central Institute of Agricultural Engineering, Carr worked on designing agricultural machinery for Indian farmers.
- Impact: His innovations in farm equipment mechanized agriculture, improving productivity and efficiency, particularly for small and marginal farmers.
- Famous Quote: "Farm mechanization is the cornerstone of modern agricultural productivity."
- Contribution: Renowned for his work on farm machinery, Dr. Mehta is a leading agricultural engineer at the Central Institute of Agricultural Engineering, focusing on mechanization for small and marginal farmers.
- Impact: His contributions to agricultural mechanization, including tools and equipment for land preparation and planting, have helped increase efficiency and reduce manual labor.
- Famous Quote: "Mechanization is the key to sustainable agricultural growth."

- Contribution: As the former chairperson of the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB), Patel played a crucial role in continuing India’s dairy revolution and improving rural livelihoods through dairy farming.
- Impact: Her leadership in the cooperative dairy sector has empowered millions of rural farmers, particularly women, in improving their income and nutrition.
- Famous Quote: "Empowering farmers through cooperatives is the path to rural prosperity."

- Contribution: Founder of the Asia-Pacific Association of Agricultural Research Institutions (APAARI) and former Director General of the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), Paroda promoted agricultural research and innovation.
- Impact: He led major initiatives in crop improvement and sustainable agriculture in India and across Asia, improving food security through research-driven strategies.
- Famous Quote: "Innovation in agriculture is key to overcoming the challenges of food security and environmental sustainability."

- Contribution: Known for his work in promoting precision agriculture and the use of modern farming technologies, Pathak is an agricultural scientist who advocated for the use of drones, GPS, and data analytics in farming.
- Impact: His efforts in advancing precision agriculture have helped optimize resource use, reduce costs, and increase productivity in India’s farms.
- Famous Quote: "Precision farming holds the key to optimizing agricultural inputs and maximizing yields."

- Contribution: A leading agricultural engineer and academic, Rathore has worked extensively on post-harvest technologies, particularly for improving food processing and reducing waste.
- Impact: His contributions to post-harvest management and processing have helped reduce food losses, improve food quality, and enhance the value chain for farmers.
- Famous Quote: "Reducing post-harvest losses is as important as increasing production in our fight against hunger."

- Contribution: A leading Indian agricultural scientist and former director of the Plant Production and Protection Division at the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the UN, Pandey contributed to global food security.
- Impact: His work has led to improvements in the resilience of crops to climate change and better farming practices globally, including in India.
- Famous Quote: "The future of agriculture lies in adapting to climate change and ensuring sustainability in food production."
- Ajay Vir Jakhar (Present): Chairman of Bharat Krishak Samaj (Farmers' Forum India), Jakhar is an advocate for sustainable farming and farmer welfare.
- Famous Quote: "Indian agriculture must shift from input-intensive to knowledge-intensive farming."
- Devinder Sharma (Present): A prominent food and trade policy analyst, Sharma advocates for farmer rights and sustainable agricultural policies.
- Famous Quote: "Agriculture must remain the primary driver of rural livelihoods."
These Indian agricultural engineers and scientists have significantly shaped the country’s agricultural landscape, addressing key challenges such as food security, water scarcity, mechanization, and climate change. Their work has not only enhanced productivity and sustainability but also helped millions of farmers improve their livelihoods, ultimately contributing to India's goal of eradicating hunger.
Note this list I did text without any particular order and best of my memory text me if you don't agree any of i mentioned or someone i Missed.
modern-era agricultural engineers, including their famous quotes and the addition of M. S. Swaminathan, one of the most significant contributors to agricultural development:
1. M. S. Swaminathan (1925–2023)
- Contribution: Known as the father of the Green Revolution in India, Swaminathan worked on introducing high-yielding varieties of wheat and rice, helping India achieve self-sufficiency in food production.
- Impact: His work prevented famines in India and contributed significantly to global food security.
- Famous Quote: "If agriculture goes wrong, nothing else will have a chance to go right."

- Contribution: Founder of International Development Enterprises (iDE), Polak developed affordable farming technologies like low-cost drip irrigation systems for smallholder farmers in developing countries.
- Impact: His innovations have helped millions of small-scale farmers in poverty-stricken regions increase their yields and income, combating hunger and improving livelihoods.
- Famous Quote: "The only way to end poverty is to create jobs and incomes for those who live on less than a dollar a day."

- Contribution: Founder of East-West Seed, Groot developed high-quality vegetable seeds suited to the tropical climates of Southeast Asia and other developing regions.
- Impact: His work has dramatically increased food security and smallholder farmer incomes by providing access to better seeds, leading to higher yields of nutritious vegetables.
- Famous Quote: "Seeds are the starting point of agriculture. They determine the quality of life for millions of small farmers around the world."

- Contribution: An agricultural economist and engineer, Adesina has been a leading figure in launching initiatives like the Alliance for a Green Revolution in Africa (AGRA).
- Impact: His work in fertilizer use, modern farming techniques, and agricultural policy has significantly increased food security across Africa.
- Famous Quote: "The future of Africa’s development depends on agriculture, and agriculture depends on youth."

- Contribution: A plant pathologist and geneticist, Ronald focuses on genetically engineering rice to be resistant to flooding and other climate challenges.
- Impact: Her work has improved crop resilience to climate change, particularly in flood-prone regions of Asia, helping to stabilize food production.
- Famous Quote: "To help feed a growing population, we need to embrace a broad array of agricultural technologies, including organic farming and genetic engineering."

- Contribution: A soil scientist and agricultural engineer, Lal has been instrumental in promoting techniques that improve soil health and carbon sequestration.
- Impact: His work is vital in combating soil degradation and enhancing agricultural productivity, while also helping mitigate climate change.
- Famous Quote: "Soil is the cornerstone of food security. We need to take care of it as we would take care of ourselves."

- Contribution: An agricultural economist and researcher, Brookes analyzes the economic and environmental benefits of genetically modified (GM) crops.
- Impact: His work has shown how GM crops contribute to increased food production and sustainability, helping to address global hunger.
- Famous Quote: "GM technology is not a magic bullet, but it can play an important part in the solution to global food security."

- Contribution: Nutritionist and agricultural engineer with extensive experience in leading food security programs in Africa, Asia, and Latin America.
- Impact: Woldt focuses on integrating nutrition-sensitive agriculture into programs to reduce hunger and malnutrition, improving food security globally.
- Famous Quote: "Sustainable agriculture is key to improving nutrition and ensuring food security for all."
- Contribution: A climate scientist and agricultural engineer, Lobell studies the effects of climate change on food production and develops strategies to improve crop yields.
- Impact: His work has influenced agricultural policies and practices to address food security in a changing climate.
- Famous Quote: "The future of food security depends on how we adapt to the changing climate."
- Contribution: An agricultural scientist and plant breeder, Ejeta developed drought-resistant and pest-resistant sorghum varieties.
- Impact: His innovations have improved food security in Africa, especially in regions where sorghum is a staple food.
- Famous Quote: "Science is a powerful tool to defeat hunger and poverty, but it requires dedication and global cooperation."
- Contribution: Founder of HarvestPlus, Bouis pioneered biofortification, improving the nutritional value of staple crops like rice, wheat, and maize by breeding them to contain higher levels of essential vitamins and minerals.
- Impact: His work has combated micronutrient deficiencies, improving health and food security in developing countries.
- Famous Quote: "Biofortification is about empowering the poor with access to better nutrition through the crops they grow and eat."
These modern engineers, along with historical figures, have made significant contributions to agriculture, helping to avert global hunger. Their work, from soil health to crop genetics and sustainable farming practices, continues to have a profound impact on ensuring food security for a growing population. Their words reflect their dedication to solving one of the world's most pressing challenges.
Note: This list is based on recent News Materials and not in particular order if you think someone is not deserved on the list or someone i missed please write down in comment.
Here’s a list of agricultural engineers whose contributions have played a significant role in transforming agriculture and helping to prevent global hunger. Their innovations have helped increase food production, improve sustainability, and ensure food security around the world:
1. Jethro Tull (1674–1741) 
- Contribution: Invented the seed drill in 1701, a major advancement in planting crops efficiently.
- Impact: This tool allowed farmers to sow seeds in neat rows, leading to higher crop yields and more efficient farming methods, thus boosting food production.

- Contribution: Developed the first commercially successful steel plow in 1837.
- Impact: Deere's plow could cut through the tough Midwestern soil, revolutionizing farming and allowing for much larger-scale production in previously difficult areas.

- Contribution: Invented the mechanical reaper in 1831, which was later improved and mass-produced.
- Impact: The mechanical reaper allowed one farmer to do the work of several, drastically improving the efficiency of harvesting grain and contributing to higher agricultural output.

- Contribution: Known as the father of the "Green Revolution," Borlaug developed high-yield, disease-resistant wheat varieties.
- Impact: His work in plant breeding helped save millions from starvation, particularly in developing countries like India and Mexico. Borlaug won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1970 for his work in combating hunger.

- Contribution: Second African American to hold a U.S. patent; invented a corn planter and a cotton planter.
- Impact: His inventions made planting crops like corn and cotton much more efficient, boosting agricultural productivity in the 19th century.

- Contribution: Developed crop rotation methods and introduced nitrogen-fixing crops like peanuts and sweet potatoes.
- Impact: Carver's work improved soil health and farm productivity, especially in the southern United States, helping to diversify crops and reduce reliance on cotton farming.
- Contribution: Though known for his work in landscape architecture, Olmsted also had a profound impact on agricultural engineering through his work in soil science and farm management.
- Impact: Olmsted's agricultural reports helped push the development of more scientific farming methods, boosting productivity and efficiency.
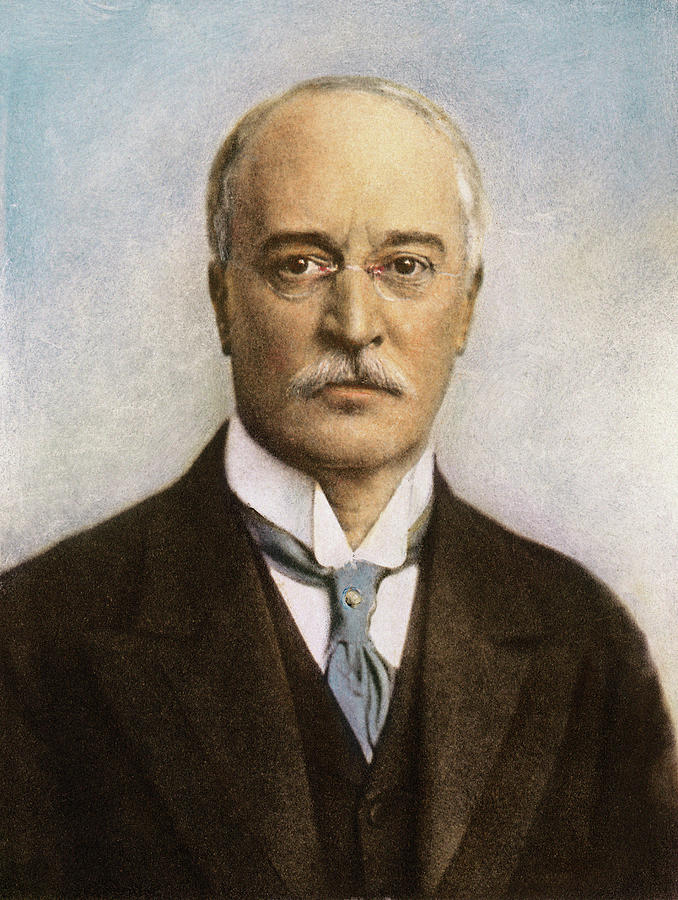
- Contribution: Invented the diesel engine.
- Impact: Diesel engines revolutionized agricultural machinery, enabling more powerful and efficient tractors and equipment, which improved farm productivity and transportation of goods.

- Contribution: Developed the Rotherham plow, an early example of mass-produced agricultural machinery.
- Impact: The Rotherham plow was cheaper and more efficient, leading to widespread adoption and improving farming efficiency in the UK.

- Contribution: Though primarily known for his safety inventions, Morgan developed a successful line of agricultural tools.
- Impact: His contributions improved agricultural safety and efficiency during the early 20th century.

- Contribution: Pioneered selective breeding of livestock.
- Impact: Bakewell's methods improved the size and quality of cattle, sheep, and horses, boosting food production and efficiency in animal husbandry.

- Contribution: Developed the Sterile Insect Technique (SIT) for pest control.
- Impact: SIT significantly reduced agricultural pests without the use of harmful pesticides, increasing crop yields while maintaining environmental sustainability.

- Contribution: Worked on soil fertility and food security, particularly in Africa.
- Impact: His efforts have helped improve agricultural productivity in some of the world's most food-insecure regions.

- Contribution: Early scholar in the Islamic Golden Age who applied scientific methods to agricultural productivity, improving irrigation and crop production.
- Impact: His advancements laid the foundation for modern agricultural engineering techniques in the Middle East and beyond.
These agricultural engineers and inventors have dramatically shaped modern agriculture, directly impacting food availability and ensuring that we can feed a growing global population. Without their contributions, global food production would have struggled to keep up with the increasing demand, leading to far more widespread hunger and chaos.

In recent years, technological advancements have transformed agricultural machinery, making farming more efficient, sustainable, and precise. These innovations are helping farmers overcome challenges like labor shortages, climate change, and the need to produce more food on limited land. Below are some of the most impactful technologies shaping the future of agricultural machinery.
1. Precision FarmingPrecision farming, also known as precision agriculture, involves using data and technology to optimize farming practices. This approach reduces waste and increases efficiency by applying resources like water, fertilizers, and pesticides only where and when they are needed.
- Drones: Agricultural drones are used to monitor crops, assess field conditions, and even apply fertilizers or pesticides in targeted areas. Equipped with sensors and cameras, drones provide real-time data on crop health, soil moisture levels, and plant growth. This enables farmers to make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control.
- GPS and Sensors: GPS technology allows farmers to create precise maps of their fields, showing variations in soil quality, crop yields, and other factors. This data, combined with sensors placed in the soil or on machinery, enables farmers to plant seeds, apply water, and spread fertilizers more efficiently. For example, variable rate technology (VRT) adjusts the amount of inputs applied across different parts of a field, optimizing resource use and improving yields.
Automation is revolutionizing the way farming is done, with autonomous machinery capable of performing tasks with minimal human intervention. These machines rely on AI, sensors, and GPS to navigate fields and carry out specific tasks such as plowing, planting, and harvesting.
- Autonomous Tractors: These driverless tractors can follow predetermined routes, ensuring that tasks like tilling or planting are completed with precision. Autonomous tractors are particularly useful for large farms where labor is scarce or expensive. They can work continuously, regardless of weather or time of day, reducing downtime and increasing productivity.
- AI-Powered Robots: Robots equipped with AI are being developed to perform a variety of tasks, from planting seeds to harvesting crops. For instance, some robots can identify and pick ripe fruits and vegetables without damaging them. AI systems can also analyze crop health and detect pests or diseases early, allowing for timely intervention and reducing crop loss.
Water management is a critical aspect of farming, especially in regions prone to drought or irregular rainfall. Smart irrigation systems use sensors, weather data, and automated controls to deliver the right amount of water to crops at the right time.
- Soil Moisture Sensors: These sensors monitor the moisture content in the soil, ensuring that crops receive water only when necessary. By avoiding over- or under-watering, smart irrigation systems help conserve water and improve crop health.
- Automated Irrigation Systems: Linked to weather forecasts and soil data, automated systems can adjust irrigation schedules based on real-time conditions. For example, if rain is expected, the system can delay watering, saving water and reducing costs.
Technological advances like these are not only improving the efficiency of farming operations but also making agriculture more sustainable. By using data and automation, farmers can reduce waste, improve yields, and minimize their environmental footprint. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will play a key role in addressing global food security and resource management challenges.
Challenges and Considerations
While agricultural machinery has brought immense benefits to farming, it also comes with challenges and considerations that need to be addressed for long-term sustainability and effectiveness. These challenges range from environmental concerns to economic factors and the adaptability of machinery for different farming scales.
1. Environmental ImpactAgricultural machinery, particularly large, fuel-powered equipment, can have significant environmental effects:
- Energy Consumption and Emissions: Many machines, especially tractors and harvesters, run on fossil fuels like diesel. This leads to carbon emissions that contribute to climate change. Additionally, the energy required to manufacture and operate this machinery adds to the carbon footprint of modern farming.
- Soil Degradation: The weight and repetitive use of heavy machinery can cause soil compaction, which reduces water infiltration and air circulation in the soil. Compacted soil is less productive, as it limits root growth and negatively affects plant health.
- Sustainable Practices: To mitigate these effects, there is a growing focus on developing more sustainable technologies, such as electric-powered machinery, fuel-efficient engines, and smaller, lighter equipment that reduces soil impact.
Agricultural machinery represents a major investment for farmers, and the financial burden can be significant, especially for small- and medium-sized farms.
- High Initial Costs: The upfront cost of purchasing advanced machinery like GPS-guided tractors, drones, and automated harvesters can be prohibitive for many farmers. Even leasing or renting machinery may not be affordable for small-scale farms.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Machinery requires regular maintenance to keep it functioning effectively. Breakdowns can lead to costly repairs and delays in critical farming operations, like planting or harvesting. Spare parts and technical expertise are often necessary, adding to the overall cost of ownership.
- Depreciation: Machinery also depreciates over time, meaning that its value decreases as it ages, potentially leading to reduced resale value or higher replacement costs.
While large commercial farms often have the resources to invest in and benefit from advanced agricultural machinery, smaller farms may face difficulties integrating such technologies:
- Scalability Issues: Many machines are designed for large fields and industrial-scale farming. Smallholders may not be able to use or justify the cost of this equipment on their smaller plots of land. However, efforts are being made to develop smaller, more affordable machines tailored to small-scale farming operations.
- Access to Technology: In some regions, especially in developing countries, farmers may not have access to the latest machinery due to poor infrastructure, lack of financial resources, or limited technical support. This can widen the gap between large, mechanized farms and smaller, manual operations.
Addressing these challenges requires a focus on innovation, cost-sharing models, and policies that support sustainable and inclusive technology adoption. By developing more eco-friendly machinery, offering flexible financial solutions, and creating equipment suitable for farms of all sizes, the agricultural sector can continue to evolve while minimizing the negative impacts.
As technology advances, the future of farming lies in precision agriculture, automation, and sustainable practices. These innovations allow farmers to optimize resource use, reduce environmental impact, and meet the challenges of feeding a growing population. However, it’s essential to balance the benefits of machinery with considerations such as environmental sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and ensuring that smaller farms can also access and benefit from these technological advancements.
Modern irrigation technology offers numerous benefits that enhance agricultural productivity, sustainability, and resource management. Here are some key advantages:
1. Water Conservation- Efficient Use: Modern systems, such as drip and sprinkler irrigation, apply water directly to the plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff.
- Reduced Waste: Precision irrigation techniques ensure that water is used only where and when needed, significantly reducing water waste.
- Optimal Water Supply: By providing the right amount of water at the right time, modern irrigation increases crop growth and yields.
- Consistency: Irrigation technology allows for consistent watering, which is crucial for maintaining healthy crops and maximizing production.
- Adaptation to Climate Change: Advanced irrigation systems can help farmers adapt to changing weather patterns and prolonged droughts by efficiently managing limited water resources.
- Storage Solutions: Technologies such as rainwater harvesting and water storage systems enable farmers to collect and store water during rainy seasons for use during dry periods.
- Reduced Erosion: Modern irrigation practices minimize soil erosion by reducing runoff and maintaining soil moisture.
- Nutrient Management: Systems like drip irrigation can be combined with fertigation (applying fertilizers through the irrigation system), allowing for better nutrient distribution and reduced leaching.
- Automation: Automated irrigation systems can be programmed to operate on schedules, reducing the need for manual labor and allowing farmers to focus on other important tasks.
- Remote Monitoring: Advanced technologies, such as sensors and smart irrigation controllers, enable farmers to monitor soil moisture levels and manage irrigation remotely, optimizing labor resources.
- Reduced Water Costs: Efficient irrigation methods lower water bills and operational costs, particularly in areas where water is expensive or scarce.
- Lower Energy Consumption: Drip and low-pressure systems can reduce energy costs associated with pumping water.
- Uniform Growth: Consistent watering leads to more uniform crop growth, which can improve the overall quality of the produce.
- Reduced Disease Risk: Proper irrigation management can help prevent water stress and associated plant diseases, leading to healthier crops.
- Sustainable Practices: Modern irrigation techniques promote sustainable agricultural practices by reducing the environmental impact of water extraction and usage.
- Biodiversity Preservation: Efficient irrigation can help maintain local ecosystems by reducing the diversion of natural water sources for agricultural use.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Modern irrigation systems can integrate with precision agriculture technologies, allowing for real-time monitoring and data analysis to optimize water use and improve decision-making.
- Adaptable Systems: Modern irrigation technologies can be scaled to fit various farm sizes, making them suitable for both smallholder and large commercial farms.
In summary, modern irrigation technology plays a crucial role in enhancing agricultural efficiency, sustainability, and resilience, benefiting farmers, the environment, and global food security.
Modern irrigation technologies offer numerous benefits that extend beyond water savings, impacting crop yields, environmental sustainability, and farm efficiency. For agriculture engineers, whether students or experienced professionals, understanding these advantages is essential for promoting and implementing these systems in real-world agricultural settings.
Water Savings
One of the most significant benefits of modern irrigation systems is their ability to conserve water. Traditional irrigation methods can waste up to 50% of water due to evaporation, runoff, and inefficient application. In contrast, technologies like drip irrigation and smart sensors ensure that water is applied precisely where and when it’s needed, reducing waste by as much as 30-60%. This is especially crucial in areas facing water shortages or in regions with unpredictable rainfall patterns. For engineers, designing systems that maximize water efficiency is key to sustainable agriculture.
Increased Crop Yields
By delivering water in a controlled and timely manner, modern irrigation systems directly enhance crop health and productivity. Drip irrigation, for instance, allows for consistent moisture levels at the root zone, promoting steady growth and improving yields by up to 40% in some crops. Smart systems that adjust irrigation based on real-time data also help avoid plant stress caused by over- or under-watering. Agriculture engineers can leverage these benefits to develop irrigation solutions that not only save water but also significantly increase agricultural output.
Reduced Environmental Impact
Modern irrigation systems play a critical role in reducing the environmental footprint of farming. Efficient water use helps prevent soil erosion, salinization, and nutrient leaching, all of which can degrade land quality over time. Furthermore, technologies that minimize energy consumption in pumping and distributing water contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions. For professionals designing eco-friendly farming systems, these benefits are increasingly important as the agricultural sector moves toward more sustainable practices.
While modern irrigation technologies offer immense potential, their widespread adoption faces several challenges. However, these challenges also present valuable opportunities for both agriculture engineering students and professionals to innovate, overcome barriers, and advance the field.
ChallengesOne of the main challenges in implementing modern irrigation systems is the high upfront cost of technology. Systems such as drip irrigation or advanced sensor networks require significant initial investments, which can be a deterrent for small-scale farmers. Additionally, there is often a lack of technical expertise among farmers and laborers to operate and maintain these sophisticated systems, particularly in developing regions. Engineers must address these gaps by designing cost-effective solutions and providing training and support for system management.
Another challenge is infrastructure limitations in rural areas, where reliable access to electricity, internet, or water sources may be insufficient to support smart irrigation systems. Overcoming these barriers will require engineers to innovate with off-grid solutions, solar-powered pumps, or decentralized water systems to ensure technology can be applied in diverse settings.
OpportunitiesDespite these challenges, the rise of modern irrigation technology presents significant career and innovation opportunities for agriculture engineers. As demand for sustainable water management solutions grows, there is a rising need for professionals who can design, implement, and manage these advanced systems. Engineers can specialize in areas such as precision agriculture, integrating technologies like AI, IoT, and automation to enhance irrigation efficiency.
Furthermore, there are increasing government incentives and funding for projects that focus on water conservation and sustainable farming practices. Engineers can collaborate with governmental and international organizations to create scalable solutions that address the water scarcity crisis. By focusing on the opportunities to innovate, future engineers can play a pivotal role in transforming agricultural practices worldwide, ensuring that farming becomes more productive, sustainable, and resilient to climate challenges.
Modern irrigation systems represent a critical innovation in the future of agriculture, offering solutions to some of the industry's most pressing challenges, such as water scarcity, declining crop yields, and environmental degradation. For agriculture engineering students and professionals, mastering these technologies is not just an academic exercise—it’s essential for driving sustainable agricultural practices in the real world. Whether through the use of sensors, AI, or precision irrigation methods, engineers are uniquely positioned to revolutionize water management in farming, ensuring higher productivity with fewer resources.
As the global demand for food continues to rise, so too does the importance of efficient irrigation systems. By embracing and advancing these technologies, agricultural engineers can play a leading role in shaping the future of farming, making it more resilient, sustainable, and productive. The future of agriculture depends on today’s engineers to develop solutions that will meet the needs of tomorrow’s world.
The Overlooked Necessity: How Engineering in Some Fields Has Fallen Behind Despite the Urgent Need for Innovation
This article is a continuation of following article Engineering fields where innovation is urgently needed but often overlooked: Engineering fields where Need For Innovation Indeed
In an age where technological innovation drives global progress, engineering has played a pivotal role in transforming industries, economies, and even societies. Yet, despite the apparent necessity, certain branches of engineering remain overlooked, leaving gaps in fields that desperately need advancement. This article explores why engineering has been missed in some faculties and how this neglect has hindered essential innovation, even in industries that stand to benefit most.
1. The Critical Role of Engineering in Innovation
Engineering, by nature, is the backbone of problem-solving in modern society. Engineers design, optimize, and innovate the tools and systems that make daily life efficient and sustainable. Whether it’s in healthcare, transportation, manufacturing, or renewable energy, engineering innovations bring about radical improvements.
However, while sectors like aerospace, IT, and biomedical engineering have seen enormous advances, other critical fields have lagged behind. The reasons for this are multi-faceted, and understanding them requires a deep dive into the factors that drive engineering development—or impede it.
2. Underfunding and Resource Allocation Issues
One of the primary reasons engineering in certain faculties has been missed is due to the uneven distribution of resources and funding. Fields like artificial intelligence, robotics, and computer science tend to attract more funding from both governments and private investors due to their high visibility and profit potential. On the other hand, critical yet less glamorous fields like civil infrastructure, environmental engineering, or agricultural technology often receive fewer resources, despite their profound societal impact.
For example, in many parts of the world, infrastructure is crumbling under the weight of time and environmental stressors, yet civil engineering faculties have not seen the same level of financial investment as the tech industry. This creates a paradox where the fields in dire need of innovation are often starved of the resources to facilitate that innovation.
3. Lack of Cross-Disciplinary Collaboration
Another reason for the neglect is the growing compartmentalization of engineering disciplines. Innovation in fields like sustainable agriculture or environmental conservation requires collaboration between environmental scientists, civil engineers, and even software engineers to create smart systems. Unfortunately, traditional academic structures often silo these faculties, making cross-disciplinary innovation more challenging.
For example, agricultural engineering—an essential field to solve global food insecurity and environmental degradation—requires knowledge from both biological sciences and mechanical engineering. However, limited collaboration across these disciplines can slow the development of effective technologies.
4. Perception and Prestige Bias
Prestige plays a significant role in driving students and funding toward certain fields. Engineering faculties associated with cutting-edge technology, like AI or nanotechnology, are often seen as more prestigious or exciting, attracting the brightest minds and most significant funding. Fields like chemical engineering, civil engineering, or even mining engineering can sometimes be perceived as outdated or less exciting, even though they are critical to solving large-scale global challenges like resource depletion, climate change, and infrastructure development.
This perception bias can create a feedback loop where less innovation occurs because fewer minds and resources are focused on the problem, further entrenching the perception that the field is stagnating.
5. Societal and Political Influences
In some cases, societal or political factors hinder engineering progress in critical fields. For example, environmental engineering, which is crucial in addressing climate change, often faces political and public resistance. Climate policies that support innovation in renewable energy, sustainable construction, or waste management can be hampered by short-term political and economic interests. Similarly, public infrastructures like roads, bridges, and public transport systems tend to suffer from underinvestment due to political cycles that prioritize more immediate, visible gains over long-term planning.
This misalignment between societal needs and political agendas can leave essential engineering faculties starved of the attention they deserve.
6. Consequences of Missed Innovation
The neglect of engineering in some faculties has had tangible consequences. For example, inadequate infrastructure and outdated water management systems in many developing nations exacerbate issues like urban flooding, water scarcity, and pollution. Meanwhile, the absence of advanced agricultural engineering in regions facing food insecurity prevents the development of innovative farming technologies that could revolutionize crop yields and resource use.
In healthcare, the missed opportunity in fields like biomedical and biomechanical engineering in certain regions means that affordable, cutting-edge medical devices and technologies remain inaccessible to many populations, even though the need for such innovation is pressing.
7. Strategies for Addressing the Gap
Addressing the gaps in overlooked engineering faculties requires a multifaceted approach:
Balanced Funding Allocation: Governments, private investors, and educational institutions must reassess funding models to ensure that underfunded but critical faculties receive appropriate financial resources. Public investment in infrastructure, for instance, should be aligned with long-term sustainability and innovation.
Encouraging Cross-Disciplinary Work: Universities should promote collaboration between engineering faculties and other scientific fields. Cross-disciplinary research centers can help facilitate the innovation needed to address complex, global challenges.
Rethinking Engineering Education: Schools and universities should reframe how they present less glamorous fields of engineering, emphasizing their critical importance and the exciting potential for real-world impact. This shift could help attract more students to fields that need innovation the most.
Policy Alignment: Policymakers must align public funding and policy incentives with long-term infrastructural and environmental goals. Prioritizing investments in sustainable development, for instance, would ensure that engineering innovations in these fields receive the support they need.
In conclusion, while engineering has fueled much of the technological progress of the modern world, critical faculties have been overlooked, even though innovation in those fields is desperately needed. From civil infrastructure to agricultural technology, missed opportunities have led to stagnation in some areas, despite the increasing urgency of the challenges these fields face.
As we move forward, balanced resource allocation, cross-disciplinary collaboration, and societal recognition of the value of these fields will be essential to ensuring that engineering can meet the diverse and pressing needs of the 21st century. Without this attention, we risk not only falling behind in innovation but also failing to solve the global challenges that will shape our future.




