User Ideas / Prospects
The future of ontological engineering is promising, especially as the need for intelligent data integration, semantic interoperability, and advanced AI capabilities continues to grow. Here are several key factors that suggest a bright future for this field:
- IoT Expansion: As the Internet of Things (IoT) expands, the need for seamless data exchange between diverse devices and systems will drive the adoption of ontological engineering.
- Data Integration: Organizations will increasingly require sophisticated data integration solutions to leverage data from various sources, making ontologies essential.
2. Advancements in AI and ML
- Enhanced AI: Ontologies can improve AI's ability to understand context and semantics, leading to more advanced and accurate machine learning models.
- Explainable AI: Ontologies can help in developing explainable AI systems by providing clear, structured representations of knowledge that can be used to explain AI decisions.
3. Growth of the Semantic Web
- Linked Data: The vision of the Semantic Web, where data is interconnected and easily accessible, relies heavily on ontologies. This will promote the growth and adoption of ontological engineering.
- Standardization: Ongoing efforts to standardize ontological languages and tools will make it easier to develop and use ontologies, furthering their adoption.
4. Industry Adoption
- Healthcare: Ontologies can play a crucial role in healthcare by enabling better data sharing, integration, and understanding of complex medical information.
- Finance: Financial institutions can use ontologies to improve data analytics, risk management, and regulatory compliance.
- Manufacturing: In manufacturing, ontologies can enhance supply chain management, product lifecycle management, and interoperability between systems.
5. Academic and Research Developments
- Research Innovations: Ongoing research in knowledge representation, reasoning, and semantic technologies will continue to advance the field.
- Education and Training: As more educational programs and resources become available, the expertise in ontological engineering will grow, fostering broader adoption.
6. Tool and Technology Improvements
- User-Friendly Tools: The development of more user-friendly and integrated tools for creating, managing, and using ontologies will lower the barrier to entry.
- Integration with AI/ML Frameworks: Better integration of ontological tools with popular AI and ML frameworks will encourage their use in AI projects.
7. Policy and Regulatory Support
- Regulatory Compliance: As regulations around data privacy, interoperability, and transparency increase, ontologies can provide structured ways to meet these requirements.
- Government Initiatives: Government initiatives promoting data sharing and interoperability in various sectors (e.g., healthcare, smart cities) will drive the adoption of ontological engineering.
- Complexity Management: Managing the complexity of large-scale ontologies will remain a challenge, requiring ongoing innovations in tooling and methodologies.
- Adoption Resistance: Overcoming resistance to adoption due to perceived overhead and the need for specialized expertise will be essential.
Conclusion:
Ontological engineering is poised to play a critical role in the future of AI, IoT, and data-driven technologies. By addressing current challenges and leveraging ongoing advancements in technology and research, the field can achieve widespread adoption and significantly impact various industries. As the need for intelligent, interoperable systems continues to grow, ontological engineering will become increasingly important, driving innovation and enabling new capabilities across diverse domains.
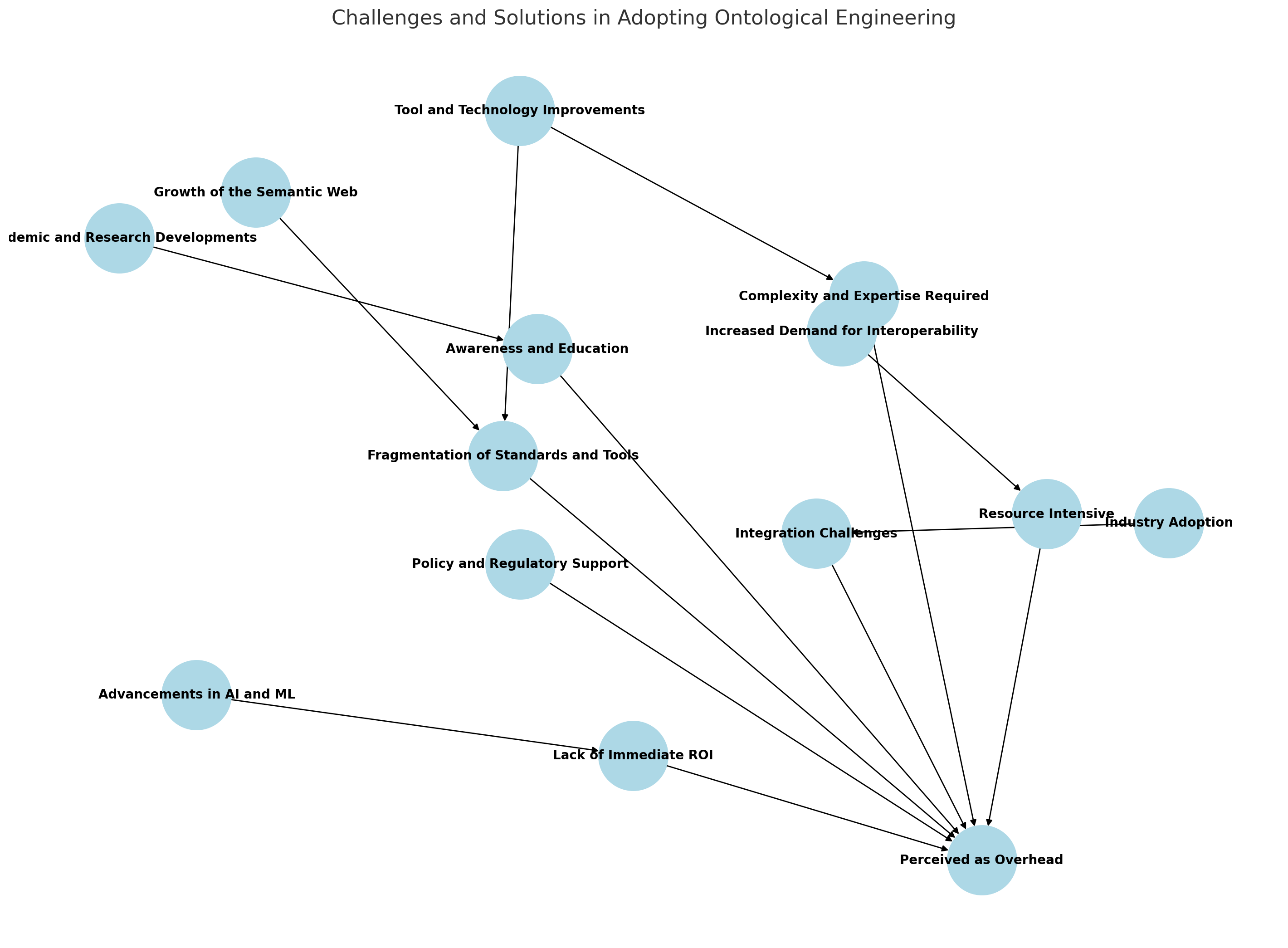
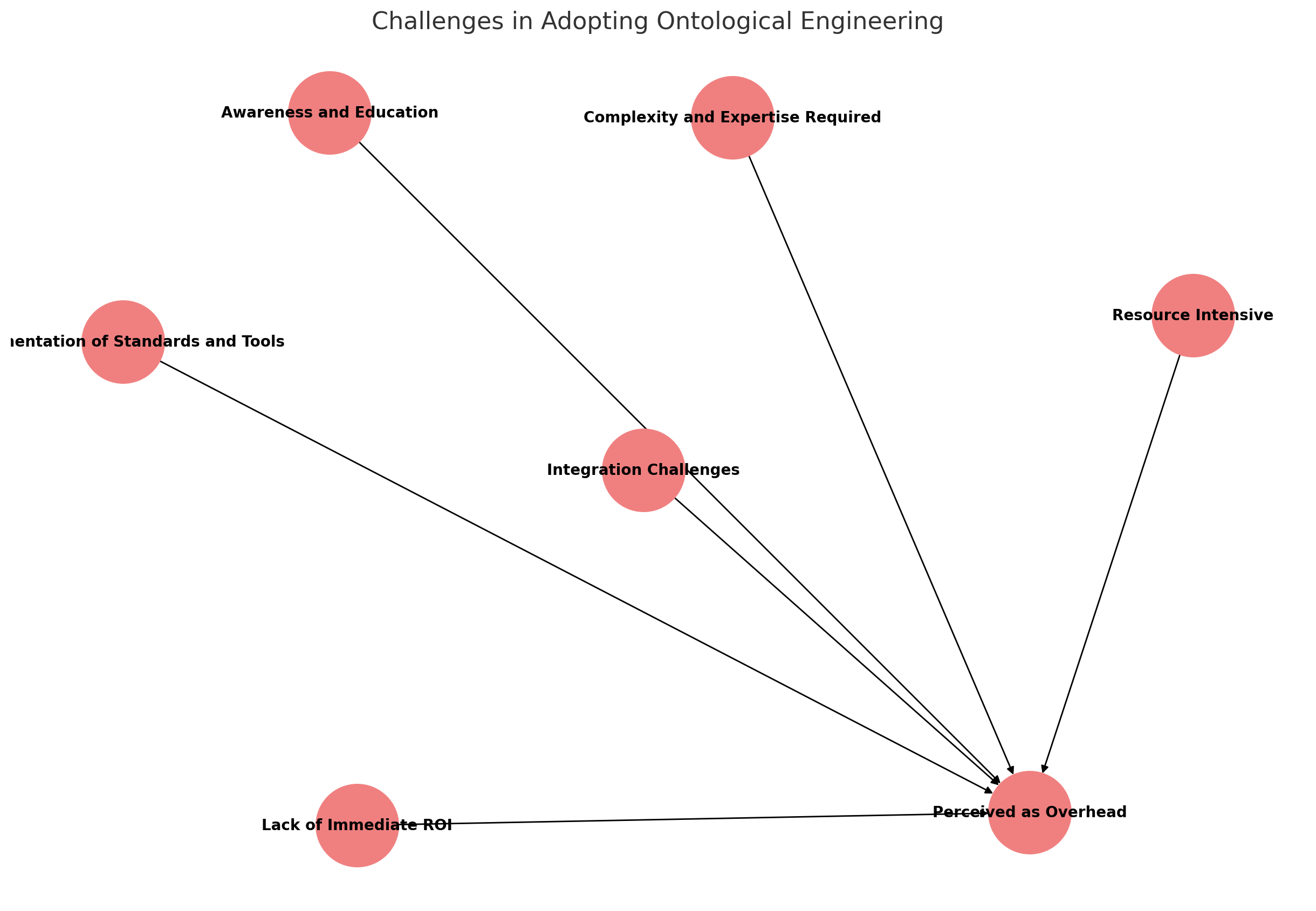
Here's a diagram that represents both the challenges and the solutions for adopting ontological engineering. The diagram illustrates how each challenge relates to the perceived overhead and how various solutions can address these challenges:
Challenges (highlighted in light blue):
- Complexity and Expertise Required
- Resource Intensive
- Lack of Immediate ROI
- Fragmentation of Standards and Tools
- Integration Challenges
- Awareness and Education
- Perceived as Overhead (central node representing the cumulative effect of all challenges)
Solutions (positioned around the challenges):
- Increased Demand for Interoperability
- Advancements in AI and ML
- Growth of the Semantic Web
- Industry Adoption
- Academic and Research Developments
- Tool and Technology Improvements
- Policy and Regulatory Support
The arrows indicate how each solution can help mitigate the respective challenges, ultimately reducing the perception of ontological engineering as an overhead. This integrated view helps visualize the multifaceted approach required to overcome the barriers to adopting ontological engineering.
Ontological engineering principles are indeed powerful and beneficial for many applications, including IoT, AI, and ML-centric websites. However, there are several reasons why these principles might not be as widely adopted as one might expect:
1. Complexity and Expertise Required
- Steep Learning Curve: Developing and maintaining ontologies require specialized knowledge and skills in formal logic, knowledge representation, and domain-specific expertise.
- Technical Expertise: Implementing ontologies often involves complex tools and languages (e.g., OWL, RDF), which can be a barrier for developers who are more familiar with traditional programming languages and frameworks.
2. Resource Intensive
- Time-Consuming: Creating detailed and comprehensive ontologies can be a time-consuming process, requiring significant effort in analysis, design, and validation.
- Costly: The development and maintenance of ontologies can be costly in terms of both human resources and computational resources.
3. Lack of Immediate ROI
- Long-Term Benefits: The benefits of ontological engineering, such as improved data integration and enhanced AI capabilities, often materialize in the long term. Many organizations prioritize short-term gains and quick wins, leading to less investment in ontology development.
- Unclear Immediate Impact: For some projects, the immediate impact of using ontologies may not be clear, making it hard to justify the investment to stakeholders.
4. Fragmentation of Standards and Tools
- Diverse Standards: The field of ontological engineering involves various standards and tools, which can be confusing and lead to fragmented efforts. This lack of a unified approach can discourage adoption.
- Tooling Issues: While there are tools like Protégé for ontology development, they might not be as user-friendly or well-integrated with mainstream development environments and workflows.
5. Integration Challenges
- Legacy Systems: Many organizations have legacy systems with data that are not designed for semantic interoperability. Integrating ontological approaches with these systems can be challenging and require significant re-engineering.
- Data Silos: Data silos within organizations can impede the effective implementation of ontologies, as data needs to be shared and linked across different departments and systems.
6. Awareness and Education
- Lack of Awareness: Many developers, data scientists, and decision-makers might not be fully aware of the benefits and capabilities of ontological engineering.
- Educational Gaps: There is a need for more educational resources and training programs to bridge the knowledge gap and promote the adoption of ontological principles.
7. Perceived as Overhead
- Initial Overhead: The initial effort required to develop and implement ontologies is often seen as overhead compared to more straightforward, immediate solutions.
- Perceived Complexity: The perceived complexity of ontological engineering can deter teams from adopting these practices, especially when simpler alternatives are available.
To promote the adoption of ontological engineering principles in IoT and AI/ML-centric websites, several steps can be taken:
- Education and Training: Increase awareness and provide training on the benefits and implementation of ontological engineering.
- Tool Development: Develop more user-friendly tools and frameworks that integrate well with existing development environments.
- Standardization: Promote standardization efforts to reduce fragmentation and provide clear guidelines and best practices.
- Showcase Success Stories: Highlight successful case studies and examples where ontological engineering has provided significant benefits.
- Collaboration: Encourage collaboration between academia, industry, and standardization bodies to drive innovation and adoption.
By addressing these challenges, the principles of ontological engineering can become more mainstream and widely adopted, leading to more intelligent, interoperable, and effective IoT and AI/ML-centric systems.
- Description: The Gene Ontology project provides a framework for the representation of gene and gene product attributes across all species. The ontology covers three domains: biological process, cellular component, and molecular function.
- Purpose: To standardize the representation of gene and gene product attributes and facilitate data integration and analysis in genomics research.
- Website: Gene Ontology
- Description: SNOMED CT is a systematically organized collection of medical terms providing codes, terms, synonyms, and definitions used in clinical documentation and reporting.
- Purpose: To support the development of comprehensive, standardized clinical terminologies for use in electronic health records (EHRs) and other healthcare applications.
- Website: SNOMED CT
- Description: DBpedia is a project aiming to extract structured content from the information created as part of the Wikipedia project. It allows users to query relationships and properties associated with Wikipedia resources.
- Purpose: To provide a semantic, linked-data version of Wikipedia, enabling easier access to structured data from Wikipedia for various applications.
- Website: DBpedia
4. FOAF (Friend of a Friend)
- Description: FOAF is an ontology for describing people, their activities, and their relations to other people and objects. It is used to create a machine-readable Web of people, documents, and relationships.
- Purpose: To enable the sharing of personal information on the web in a way that is understandable by machines, facilitating social networking and other applications.
- Website: FOAF Project
5. Protégé
- Description: Protégé is an open-source ontology editor and framework for building intelligent systems. It is widely used for creating and managing ontologies and supports a variety of ontology languages.
- Purpose: To provide a platform for developing, sharing, and publishing ontologies, supporting a range of users from domain experts to ontology engineers.
- Website: Protégé
- Description: GoodRelations is an ontology for e-commerce, enabling the representation of products, prices, and business relationships in a structured and machine-readable way.
- Purpose: To improve the efficiency and effectiveness of e-commerce transactions by providing a standard way to describe product offerings and business interactions.
- Website: GoodRelations
- Description: The OBO Foundry is a collaborative effort to develop a family of interoperable ontologies that are both logically well-formed and scientifically accurate.
- Purpose: To create a suite of orthogonal, interoperable, and scientifically accurate reference ontologies for the biological and biomedical sciences.
- Website: OBO Foundry
8. BFO (Basic Formal Ontology)
- Description: BFO is a top-level ontology designed to support domain ontologies in scientific research. It provides a framework for the development of domain-specific ontologies.
- Purpose: To ensure interoperability between ontologies used in scientific research and provide a common basis for domain ontologies.
- Website: Basic Formal Ontology
These projects illustrate the diverse applications and significant impact of ontological engineering across various fields, from healthcare and life sciences to e-commerce and social networking.
if you wondering why/how these projects i consider as Ontological Engineering Project than here are the reasons.
These projects can be classified as ontological engineering projects because they all involve the creation, maintenance, and application of ontologies. Here's how each project fits into the framework of ontological engineering:
1. Gene Ontology (GO)
- Classification: Domain-specific ontology for genomics and molecular biology.
- Reason: GO provides a structured vocabulary for gene and gene product attributes, enabling consistent data annotation and integration across different species and databases.
2. SNOMED CT (Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine—Clinical Terms)
- Classification: Clinical ontology for healthcare and medicine.
- Reason: SNOMED CT systematically organizes medical terms and relationships, facilitating standardized clinical documentation and interoperability in electronic health records.
3. DBpedia
- Classification: General-purpose ontology for structured data extraction from Wikipedia.
- Reason: DBpedia extracts structured information from Wikipedia, creating an ontology that represents relationships between concepts and entities for use in semantic web applications.
4. FOAF (Friend of a Friend)
- Classification: Social ontology for describing people and their relationships.
- Reason: FOAF provides a vocabulary for describing personal information and social networks in a machine-readable format, enabling interoperability across social web applications.
5. Protégé
- Classification: Ontology development tool.
- Reason: Protégé is an ontology editor and framework that supports the creation, management, and sharing of ontologies, making it a central tool in ontological engineering.
6. GoodRelations
- Classification: E-commerce ontology for product and business information.
- Reason: GoodRelations provides a standardized vocabulary for representing product offerings, prices, and business relationships, facilitating semantic data exchange in e-commerce.
7. Open Biological and Biomedical Ontology (OBO) Foundry
- Classification: Consortium for developing interoperable ontologies in biology and biomedicine.
- Reason: The OBO Foundry supports the creation of a suite of interoperable ontologies for biological and biomedical research, ensuring logical consistency and scientific accuracy.
- Classification: Top-level ontology framework.
- Reason: BFO provides a foundational ontology that supports the development and integration of domain-specific ontologies, ensuring interoperability and consistency in scientific research.
- Creation of Structured Frameworks: Each project involves developing a structured representation of concepts and their relationships within a specific domain.
- Standardization: These ontologies provide standardized vocabularies that facilitate consistent data annotation, integration, and retrieval.
- Interoperability: The ontologies enable different systems and organizations to understand and use data consistently, promoting interoperability.
- Knowledge Representation: The projects formalize knowledge within a domain, making it machine-readable and enabling automated reasoning and advanced data processing.
- Tool Support: Tools like Protégé are essential for building, managing, and sharing ontologies, highlighting the practical aspect of ontological engineering.
By addressing these key elements, each project exemplifies the principles and practices of ontological engineering, contributing to the broader goals of improving data integration, sharing, and utilization across various domains.
Ontological Engineering as a Next Step in Computer Science and Engineering.
Introduction
In the realm of information science and artificial intelligence, ontological engineering plays a crucial role in shaping how systems understand and interpret data. Ontological engineering involves the creation, maintenance, and application of ontologies—structured frameworks that define the relationships between concepts within a domain.
What is Ontological Engineering?
Ontological engineering is the process of developing ontologies. An ontology is a formal representation of a set of concepts within a domain and the relationships between those concepts. It provides a shared vocabulary that can be used to model the domain and enables different systems and organizations to understand and use the data consistently.
Key Components of Ontologies
- Classes (or Concepts): These are the fundamental building blocks representing entities within a domain.
- Relations: These define how classes are related to one another.
- Attributes: These provide additional information about classes and relations.
- Instances: Specific examples of classes.
- Axioms: Rules that define the properties and constraints of the ontology.
- Interoperability: Facilitates communication between disparate systems by providing a common understanding of data.
- Data Integration: Enhances the ability to combine data from different sources, ensuring that the data is interpreted correctly.
- Knowledge Sharing: Promotes the sharing of domain knowledge across various platforms and applications.
- Improved Search and Retrieval: Ontologies improve the accuracy and efficiency of information retrieval systems by providing context to data.
Applications of Ontological Engineering
- Semantic Web: Ontologies are fundamental to the Semantic Web, which aims to make internet data machine-readable.
- Artificial Intelligence: Ontologies enable AI systems to understand and reason about data more effectively.
- Healthcare: Used to integrate and interpret medical data from various sources, improving patient care and research.
- E-commerce: Enhances product search and recommendation systems by understanding product attributes and customer preferences.
Challenges in Ontological Engineering
- Complexity: Building comprehensive ontologies can be complex and time-consuming.
- Scalability: Ensuring ontologies can scale with growing data and requirements.
- Maintenance: Keeping ontologies up-to-date with evolving domain knowledge.
- Consistency: Maintaining consistency in large and distributed ontologies can be difficult.
- Ontology Editors: Tools like Protégé help in the creation and management of ontologies.
- Reasoners: Software like Pellet or Hermit that can infer logical consequences from an ontology.
- Ontology Languages: OWL (Web Ontology Language) is commonly used for defining ontologies.
Conclusion
Ontological engineering is a vital discipline in the information age, enabling systems to understand, integrate, and utilize data effectively. As technology continues to evolve, the role of ontologies in bridging data and knowledge will become increasingly significant, driving advancements in AI, data science, and beyond.
The term "ontology" has its roots in philosophy but has also found significant application in information science and technology. Here’s an explanation of its meaning in both contexts:
Philosophical Context
- Definition: In philosophy, ontology is the branch of metaphysics concerned with the nature and relations of being. It deals with questions about what entities exist or can be said to exist and how such entities can be grouped and related within a hierarchy.
- Focus: Ontology in philosophy is focused on the study of existence, reality, and the nature of being.
- Key Questions: Examples include "What is existence?", "What does it mean for something to be?", and "How do different entities relate to each other within the framework of reality?"
Information Science and Technology Context
- Definition: In information science and technology, an ontology is a formal, explicit specification of a shared conceptualization. It provides a structured framework to model a domain by defining the types of entities, their properties, and the relationships between them.
- Focus: Ontology in this context is focused on the representation and organization of knowledge to enable better data sharing, integration, and analysis.
- Components:
- Classes (or Concepts): The categories of things in the domain.
- Relations: How classes are related to one another.
- Attributes: Properties of classes and relations.
- Instances: Specific examples of classes.
- Axioms: Rules that define the properties and constraints of the ontology.
Etymology
- Origin: The word "ontology" is derived from the Greek words "ontos" (being) and "logia" (study of). Thus, it literally means the study of being or existence.
Usage in Technology
- Semantic Web: Ontologies are crucial for the Semantic Web, allowing data to be shared and reused across application, enterprise, and community boundaries.
- Artificial Intelligence: They enable AI systems to understand and reason about data, providing a foundation for knowledge representation.
- Data Integration: Ontologies help in combining data from different sources, ensuring that the data is interpreted correctly and consistently.
Example in Technology
Imagine a medical ontology that includes concepts such as diseases, symptoms, treatments, and relationships like "has symptom" or "is treated by." This ontology would help different healthcare systems and applications share and understand medical data consistently, improving patient care and research.
In summary, ontology, whether in philosophy or technology, is about understanding and defining the nature and structure of entities and their relationships. In technology, this understanding is formalized to facilitate better data management, integration, and utilization.