User Ideas / Prospects
.jpeg)
Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) are omnipresent. Whether through satellites or smartphones, from medical devices to high-speed internet, ECE energizes the contemporary world. So, what do electronics and communication engineers even do?
We guide future engineers in making their careers. If you're interested in ECE, this guide will explain ECE in the most straightforward and basic way possible.
The Core of ECE
Electronics and communication engineers develop and maintain electronic systems. They are responsible for ensuring that communication is seamless, that signals are processed accurately, and that data is transmitted reliably. They are the bridge between hardware and software, ensuring perfect technology work.
1. Designing and Developing Electronic Circuits
All the gadgets you use—smartphones, laptops and even smartwatches—use electronic circuit boards. Engineers create these circuits to do one specific task. They design new devices using semiconductors, microprocessors and sensors.
2. Communication Systems and Networks
Now imagine there was no internet, mobile network, or satellite communication. ECE professionals ensure that these systems operate smoothly. They deal with signal transmission, the optimization of networks, and technology for wireless communications. Their expertise, whether 5G, optical fibre communication, or satellite telecommunications, keeps us connected.
3. Embedded Systems and IoT
Your smart TV, home automation system, or even a new car are all equipped with embedded systems. These are small bits of computing inside devices. They are designed and programmed by ECE engineers to make things more efficient. The Internet of Things (IoT) makes it a more interesting field to this обо.
4. Robotics and Automation
This is no longer science fiction: Robotics is a reality. Computer scientists create smart devices that can serve in various industries, health, or space. They combine sensors, AI, and machine learning to develop automated systems that increase efficiency.
5. Machine Learning and Signal Processing
Data is the new gold. Signals—audio, video, and digital data—are analyzed and processed by engineers to enhance communication and security. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning have broadened the horizons of ECE by enabling systems to become intelligent and more endurable.
6. Semiconductor and Chip Design
Microchips are the stuff of the digital age. Engineers in this field focus on making highly efficient and compact chips, from computer processors to memory storage. This domain is central to improvements in computing and artificial intelligence.
Career Opportunities in ECE
Electronics and Communication Engineering is a vast field. Graduates can find employment in a wide array of industries, such as:
- Telecommunication — Mobile networks, satellite communication, fibre optics
- Consumer Electronics – Smartphones, laptops, wearables
- Aerospace & Defense – Radar system, navigation, military communication
- Health Technology – Medical imaging, diagnostic devices, wearable health monitors
- Automotive – There are electric vehicles, automation, and sensor integration
- Data Science and AI – Intelligent systems, predictive modelling, neural networks
With technology growing, ECE experts are in demand everywhere in the world. It sets the stage for either working at a tech giant or pursuing your innovations.
Why is ECE the Future?
We live in an increasingly digital world. As AI, 5G, smart devices, and automation revolutionize industries, ECE engineers lead the way. This is not a field of upgraded gadgets. It's about creativity, excellence and solving real-world problems.
At Engineer's Heaven, we provide resources and training for Engineers. From project ideas to interview tips to career advice, our platform has you covered.
Conclusion
Communication and Electronics Engineering is a very colourful and entertaining area of science. It combines creativity with technical know-how at the heart of innovative technology. If you like innovation and solving problems, consider an ECE career. Got more questions about the world of engineering? Go to Engineer's Heaven and begin your journey into the future!
(Disclaimer: This statistics could be different in different part of World and Different timeline. this statistics has been generated based on data available till 2025 or relavant time span.)

Agricultural Engineering is an interesting and developing field. This field combines technology with agriculture. The career provides vast opportunities. Many students ponder over the highest salary in this career line. Let's discuss the earning potential of agricultural engineers in detail.
The role of agricultural engineers
Agricultural engineers solve farm problems. They design tools and systems to increase crop production. Their work helps farmers save time and effort. They also deal with irrigation, machinery, and soil conservation.
The job is highly technical. It demands an in-depth knowledge of engineering and agriculture. This combination of knowledge makes agricultural engineers highly prized in the labor market.
Factors Influencing Salary
The salary of an agricultural engineer depends on several factors:
● Experience: The more experience, the more pay. Those who are at the top of the career ladder are paid way more than those who are newly qualified engineers.
● Education: Master’s or doctorate results in better jobs and higher pay. Specialized roles are available to those who have advanced knowledge.
● Location: The salaries also differ in countries and cities, as illustrated by the following table. Technicians in developed countries earn more than those in developing countries.
● Industry: Employment in private entities is more often well compensated than in government organizations. In general, research and consultancy positions are also paid better.
● Specialization: Proficiency in automation or biotechnology can raise income.
Average Salary of an Agricultural Engineer
Agricultural engineers are well-remunerated for their service. According to the United States, the average salary per annum is approximately seventy-five thousand eight hundred dollars. In India, it is between 300,000 and 1,000,000 rupees per year. Other countries have the same range depending on the economic situation in the countries in question.
However, some engineers earn way above the average. That is why they are different—their experience, education, and skills.
The Highest Pay Scale of Agricultural Engineers
The highest salary of an agricultural engineer is quite good. In some countries, senior engineers can earn as much as $150,000 or more per year. Such salaries are, for example, offered in international companies or in international research institutions.
The maximum remuneration paid to employees in India is up to ₹ 25-30 lakhs per annum. Such jobs are few but achievable. They normally have years of experience. High-paid jobs also include many privileges such as bonuses and profit sharing.
Here are some of the best employers in this field:
● Government Agencies: They offer long-term employment with reasonable wages. They may be paid less than in private firms due to the fact that the government has limited financial resources.
● Private Companies: Some industries, such as producers of agricultural equipment and food processing industries, are affected by this. They occasionally offer better remuneration for their employees.
● Research Institutions: Companies such as the USDA or ICAR employ engineers for higher research purposes.
How to Make the Maximum Pay
Achieving the highest salary will require you to put in effort. Here are some tips to increase your potential earnings:
● Advanced Education: A master's or PhD education can make the difference.
● Develop Specialized Skills: Study robotics, AI, or sustainable farming.
● Gain Experience: Work on various projects.
● Network: Connect with industry leaders to discover opportunities.
● Stay Updated: Keep learning about new technologies and methods.
The Global Demand for Agricultural Engineers
Agricultural Engineers are in demand worldwide. Countries with advanced farming industries often hire them. Developing nations also need engineers for rural development. This global demand creates many high-paying jobs.
Additionally, the focus on sustainable farming has increased demand. Engineers who work on eco-friendly solutions are especially valued.
Engineer’s Heaven is the perfect place to start your journey. Whether you’re a student or a professional, you’ll find valuable insights. Join a community of like-minded individuals and explore endless possibilities.
Remember, the future of farming depends on innovation. The agricultural engineer can lead the charge. Explore this rewarding career with help from Engineer's Heaven. Start today and take the first step toward a bright future!
Sources: https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/finding-a-job/careers-in-agriculture-engineering?
https://www.shiksha.com/engineering/agriculture-farm-engineering-career-chp#:~:text=A.,ten%20lakh%20rupees%20per%20year.
https://collegedunia.com/courses/bachelor-of-technology-btech-agricultural-engineering/salary-of-an-agricultural-engineer
(Disclaimer: This statistics could be different in different part of World and Different timeline. this statistics has been generated based on data available till 2024 or relavant time span.)
India has been home to numerous visionary engineers, scientists, and technologists who have contributed significantly to the nation's development. Here’s a list of other notable individuals who have dedicated their lives to engineering and technology-based development in India:
1. Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam (1931–2015)

- Contributions: Known as the “Missile Man of India,” Dr. Kalam played a key role in India’s missile development programs, including AGNI and PRITHVI missiles. He also contributed to India’s nuclear program and the Pokhran-II nuclear tests in 1998.
- Role: He served as the 11th President of India (2002–2007) and was instrumental in advocating for India’s self-reliance in defense technologies.
- Legacy: His work in aerospace engineering and defense research continues to inspire engineers and scientists across the country.
2. Dr. Vikram Sarabhai (1919–1971)

- Contributions: Often regarded as the father of India’s space program, Dr. Sarabhai was the founder of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). He was instrumental in developing India’s first satellite, Aryabhata, and initiating India’s space exploration journey.
- Role: He emphasized the importance of space technology for the socio-economic development of India, pioneering remote sensing and satellite communications for India’s progress.
- Legacy: His vision laid the foundation for India becoming a global player in space exploration.
3. E. Sreedharan (b. 1932)

- Contributions: Known as the "Metro Man of India," Sreedharan played a pivotal role in revolutionizing urban transportation through the Delhi Metro project, which became a model of public transportation infrastructure in India.
- Role: He led several key projects, including the Konkan Railway and various other metro systems in cities like Kochi and Lucknow.
- Legacy: His work is hailed for its timely execution and cost efficiency, transforming the mass transit systems in Indian cities.
4. Satish Dhawan (1920–2002)

- Contributions: Satish Dhawan succeeded Vikram Sarabhai and was the third Chairman of ISRO. Under his leadership, ISRO made remarkable progress, including the successful Aryabhata satellite launch and subsequent space missions.
- Role: He promoted self-reliant space technology, focused on satellite launch vehicles like SLV and PSLV, and developed India’s space capabilities.
- Legacy: The Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota is named in his honor, signifying his contributions to India's space success.
5. Dr. M. Visvesvaraya (1861–1962)

- Contributions: As mentioned earlier, Sir M. Visvesvaraya made lasting contributions to infrastructure development, including water management, dams, and the promotion of technical education in India.
- Legacy: His legacy is marked by the establishment of dams and irrigation projects that still benefit the nation today. He is commemorated every year on Engineers' Day.
6. Dr. Homi J. Bhabha (1909–1966)

- Contributions: Dr. Bhabha is known as the father of India’s nuclear program. He was the key architect of India's atomic energy program and established the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC).
- Role: He initiated India’s nuclear research, laying the foundation for the country’s nuclear energy and weapons programs. His efforts enabled India to become a nuclear-capable state.
- Legacy: His pioneering work has given India the ability to harness nuclear technology for both power generation and defense purposes.
7. Verghese Kurien (1921–2012)

- Contributions: Known as the Father of the White Revolution, Kurien’s Operation Flood made India the largest producer of milk in the world. His efforts revolutionized India's dairy sector by introducing modern dairy engineering techniques.
- Role: As the founder of Amul, he created a supply chain model that empowered rural dairy farmers and transformed India into a self-sufficient dairy nation.
- Legacy: Kurien’s model continues to uplift the agricultural economy, impacting millions of lives through dairy cooperatives.
8. Dr. G. Madhavan Nair (b. 1943)

- Contributions: Dr. Nair served as the Chairman of ISRO and led many successful missions, including the Chandrayaan-1 mission in 2008, which discovered water molecules on the Moon’s surface.
- Role: He also led the successful launch of 11 satellites in a single mission and developed the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) program.
- Legacy: His contributions have helped India’s space research soar to greater heights, making ISRO a global player in space exploration.
9. Dr. M. S. Swaminathan (1925-2023)

- Contributions: Considered the Father of the Green Revolution in India, Dr. Swaminathan played a crucial role in agricultural engineering by developing high-yielding varieties of wheat and rice, which helped India overcome famine-like situations and become food self-sufficient.
- Role: He focused on agricultural technology and scientific farming methods, which significantly increased India’s food production.
- Legacy: His efforts have led to improved food security in India, saving millions from hunger and transforming the agricultural landscape.
10. Sam Pitroda (b. 1942)

- Contributions: Sam Pitroda is known as the pioneer of India’s telecommunications revolution. As an advisor to Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi, he was instrumental in laying the foundation of India’s telecom and IT industry.
- Role: He established the Center for Development of Telematics (C-DOT) and played a key role in the development of India’s telecom infrastructure, including the introduction of public call offices (PCOs) in rural India.
- Legacy: His contributions have helped propel India into the information age, making telecommunications accessible to millions across the country.
11. Dr. Anil Kakodkar (b. 1943)
- Contributions: A prominent nuclear scientist, Dr. Kakodkar was instrumental in India’s nuclear energy development. He served as the Chairman of the Atomic Energy Commission of India and oversaw several significant nuclear projects.
- Role: He played a key role in India’s 1998 nuclear tests (Pokhran-II) and the development of nuclear reactors for peaceful energy generation.
- Legacy: His leadership in nuclear research and energy policy has made India a prominent player in the global nuclear energy sector.
12. Dr. Raghunath Anant Mashelkar (b. 1936)

- Contributions: Dr. Mashelkar is a renowned chemical engineer and former Director-General of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR). He promoted innovation, patents, and intellectual property rights (IPR) for Indian scientific research.
- Role: He played a crucial role in shaping science and technology policies in India and advocated for inclusive innovation to benefit the common people.
- Legacy: His contributions to scientific research and innovation policy continue to impact industrial growth and technological progress in India.
13. Dr. Rajagopala Chidambaram(b. 1943)
- Contributions: His work in designing and developing the nuclear devices tested during Pokhran-II was a landmark achievement in India's defense and scientific history.
- Role: He played a crucial role in He played a crucial role as the Chairman of the Atomic Energy Commission of India and was the Chief Scientific Adviser to the Government of India during this period..
- Legacy: He served as the head of the Atomic Energy Commission of India, overseeing India's atomic energy research and policy. Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India: Dr. Chidambaram served as the Principal Scientific Adviser (PSA) to the Government of India, a prestigious role in which he guided national policies on science, technology, and innovation. Director of Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC): Before becoming Chairman of the Atomic Energy Commission, he was the Director of BARC, one of India’s leading nuclear research centers. Under his leadership, BARC expanded its research and technological contributions in nuclear energy and defense. Dr. Rajagopala Chidambaram is regarded as a key architect of India's nuclear program, contributing both to its strategic defense capabilities and nuclear energy development. His leadership in the Pokhran-II tests and his commitment to scientific research have made him a towering figure in Indian nuclear science and policy.
His advocacy for self-reliance in technology, his contributions to scientific development, and his leadership in nuclear physics have left an indelible mark on India's strategic and scientific landscape.
- Contributions: Mr. Dilip Asbe is the MD & CEO of National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI). Prior to this he was the Chief Operating Officer (COO) of NPCI. He has played a pivotal role in designing, building, operationalisation and management of large scale innovative payments processing platforms like Unified Payments Interface (UPI), Bharat Interface for Money (BHIM), Immediate Payment Service (IMPS) and India’s home grown card network RuPay.
- Role: A formidable leader to the core, he has ensured the delivery of processing over 1 billion transactions a month with good mentoring of teams. Recently, he was awarded the ‘Changemaker of the Year’ award for the revolutionary product UPI which he spearheaded, by one of the leading business dailies. Further, very recently he was awarded the ET award 2018 for Policy Change agent of the year award for UPI.

- Contributions: Vishal Kanvaty serves as the Chief Technology Officer at National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), where he has made significant contributions over the past 7+ years. Notably, he played a crucial role in developing the highly scalable mobile payment platform, Unified Payments Interface (UPI).
- Role: Vishal has been instrumental in developing AI-driven models that effectively mitigate fraud in the payments industry. Additionally, he has been leading the Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) initiatives at NPCI, further solidifying his position as a pioneer in the field of payments technology.
- Contributions: With over 30 years of experience in the IT sector, Saiprasad’s expertise spans various high-impact roles across prominent organizations. Before joining NPCI, he was a key contributor at Dena Bank, managing critical IT operations and leading significant projects. His career also includes notable tenures at Unit Trust of India Technology Services Ltd. and Piramal Technology Systems, where he played a crucial role in transformative technology solutions and systems management.
- Role: Mr. Saiprasad Nabar joined the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) on October 7, 2011, as the Head ofNFS Applications & Switching Technology. He currently serves as the Chief Platform Officer, playing a vital role in driving technological advancements and strategic platform initiatives essential to NPCI’s mission of enhancing India’s digital payments ecosystem.
These pioneers have made remarkable contributions to engineering and technology in India, helping to transform the nation in various sectors, including space, nuclear energy, transportation, agriculture, telecommunications, and public infrastructure. Their legacies continue to shape India's progress toward becoming a global leader in innovation and technology.
Note:- This order is just i put as I able to remind names not in order of measurement of contribution.
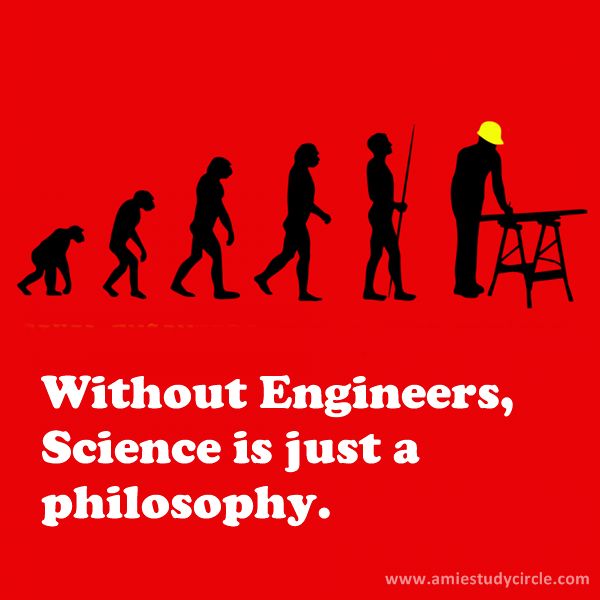
Image Describes Human Civilization WIth and Without Engineers and all the advancement through them
Life without engineers would be drastically difficult, as engineers play a critical role in shaping the world we live in. Here are some key aspects that would be affected:
Infrastructure: Cities would lack the essential infrastructure like bridges, roads, tunnels, and buildings. The absence of civil engineers would mean no skyscrapers, efficient transportation systems, or safe residential structures.
Technology: Without engineers, technological advancements would be minimal. Computers, smartphones, and the internet—integral to modern communication—wouldn't exist.
Energy: Our energy systems, from electricity grids to renewable energy technologies like solar panels and wind turbines, rely heavily on engineers. Without them, reliable power supply and modern conveniences like electric lighting and heating would be unavailable.
Healthcare: Medical devices, diagnostic equipment, and pharmaceutical production processes, all designed and maintained by biomedical and chemical engineers, would be non-existent. This would significantly hinder medical progress and healthcare quality.
Transportation: Cars, airplanes, trains, and ships, all products of mechanical and aerospace engineering, would not exist. Travel would be limited to primitive methods, drastically slowing down global mobility.
Manufacturing: The production of goods, from food processing to electronics, relies on sophisticated machinery and automation designed by engineers. The efficiency and scale of modern manufacturing would be impossible without their contributions.
Water and Sanitation: Engineers design systems to provide clean water and manage waste. Without these systems, public health would be severely compromised.
Communication: The development of telecommunication systems, including satellites and fiber optics, would stall without engineers, limiting global connectivity.
Engineers are the backbone of innovation and functionality in society. Their absence would result in a world where basic needs are hard to meet, and technological progress is stunted.
So thanks to all the engineers to make Human Civilization more wonderful, good and easy going with full of facility and luxury.
Long Live Engineering
Now before you readers get this to some other way I must want to admit that. Science itself is more than just a philosophy. Even without direct engineering applications, scientific research advances our understanding of the universe, which is valuable in its own right. Pure science often drives innovation by pushing the boundaries of knowledge, which engineers later translate into practical applications.
The relationship between science and engineering is symbiotic rather than hierarchical. Engineers rely on scientific discoveries to innovate, and scientists often depend on engineering tools and technologies to conduct research. For example, advances in materials science or biomedical research often require sophisticated engineering tools and techniques.
And like wise Scientific research often relies on advanced tools and instruments, many of which are developed by engineers. For instance, modern physics would be unimaginable without the sophisticated particle accelerators designed by engineers, which allow scientists to probe the fundamental nature of matter.
Many scientific fields, such as astronomy or genomics, generate vast amounts of data. Engineers develop the technologies—like telescopes, sequencing machines, and data processing software—necessary for collecting, storing, and analyzing this data, enabling scientific discoveries.
Engineering innovations frequently lead to new experimental techniques. For example, advancements in materials science, a branch of engineering, have allowed scientists to explore the properties of new materials, leading to discoveries in nanotechnology and quantum computing.
Science provides the theoretical foundation and discoveries that engineers use to develop new technologies, while engineering provides the tools, techniques, and innovations that enable scientific research to advance. Both fields are crucial for progress, and each drives the other forward, leading to the continuous evolution of knowledge and technology.
So Science and Engineering both are interdependent wise versa.
but still ...
Engineers are responsible for applying scientific principles to solve real-world problems. Science provides the foundational knowledge, but engineering turns that knowledge into practical solutions, such as technology, infrastructure, and systems that benefit society. Without engineering, scientific discoveries might remain theoretical concepts, with limited impact on everyday life.
Engineers bridge the gap between scientific theory and practical implementation. For instance, while scientists may understand the principles of electromagnetism, it’s engineers who design and build electrical grids, smartphones, and computers. This practical application is what transforms scientific ideas into tangible realities.
Engineering is crucial for innovation and technological progress. Many of the advancements we associate with modern science—such as medical devices, renewable energy systems, and communication technologies—are the result of engineering efforts to harness scientific discoveries.
So "Without Engineers, Science Is Just a Philosophy" is a significant truth.
so I wrote this article to dedicate my gratitude to all of the Engineers who work hard on big important project with knowing that their name probably not going to shine only money as per market norm they are going to get but still they did work harder and smarter to make sure project don't get failed.
Long Live Engineering.