User Ideas / Prospects
Civil engineering is often called the foundation of a nation’s progress, because it shapes the very roads we walk on, the bridges we cross, the dams that irrigate our fields, and the buildings where we live and work. In India, civil engineers have been silent warriors of nation-building since independence, contributing to large-scale infrastructure, sustainable growth, and the transformation of society.
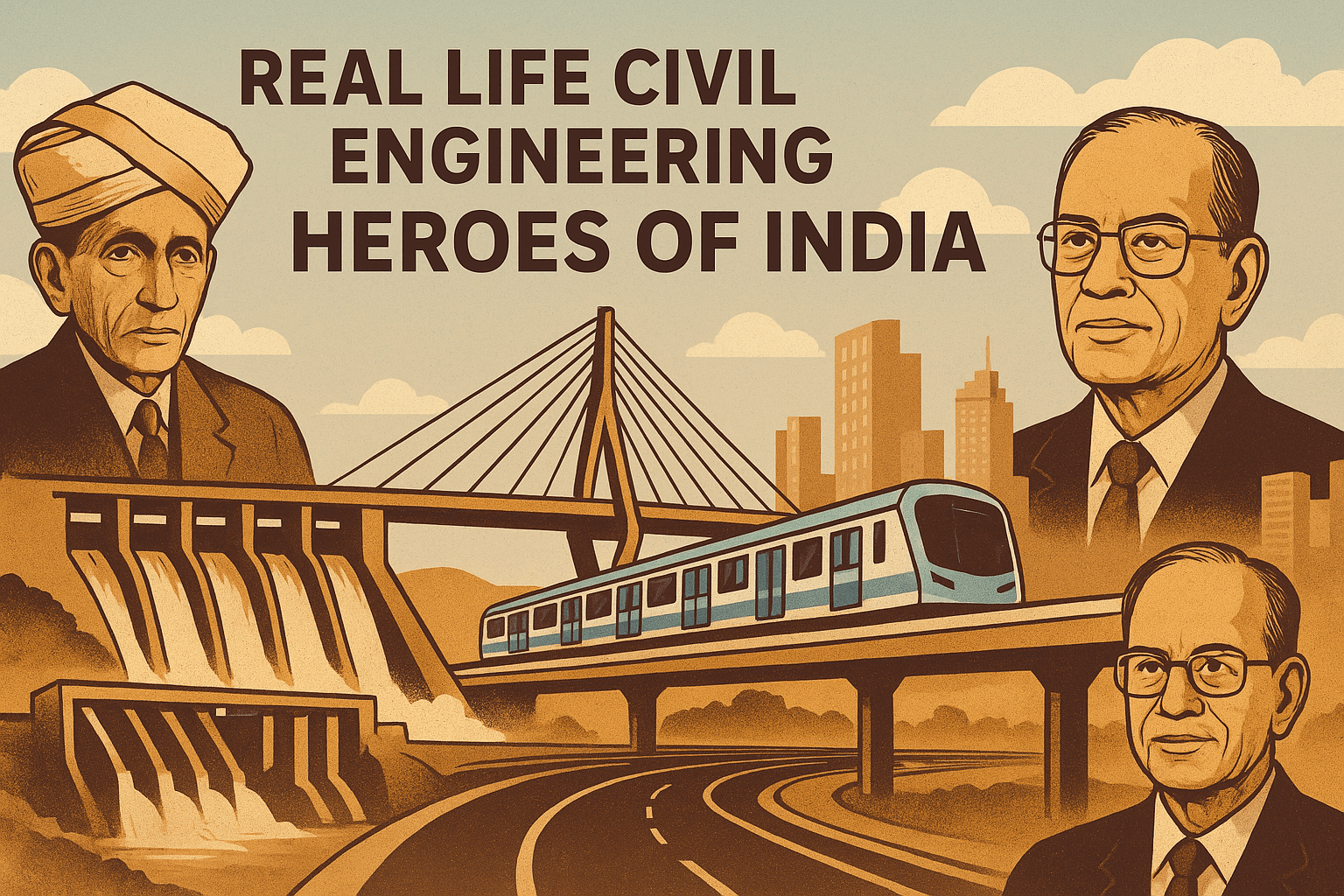
This article celebrates some of the real-life Civil Engineering heroes of India — professionals who didn’t just work for money, but dedicated their knowledge and vision toward building the nation.
Notable Civil Engineers Who Built India 1. Sir M. Visvesvaraya (1861–1962)

Contribution: "Father of Modern Civil Engineering in India," designer of Krishna Raja Sagara Dam, pioneer in irrigation and flood control.
Publications: Planned Economy for India (1934).
Quote: “Remember, your work may be only to sweep a railway crossing. But, it is your duty to keep it so clean that no other crossing in the world is as clean as yours.”
2. E. Sreedharan (1932– )

Contribution: “Metro Man of India,” leader of the Konkan Railway and Delhi Metro.
Publications: Restless: Memoirs of E. Sreedharan (2019).
Quote: “Commitment, accountability, and integrity are not optional in engineering—they are essential.”
3. Dr. Ajudhiya Nath Khosla (1892–1984)
Contribution: Visionary behind Bhakra Nangal Dam, pioneer in irrigation and hydropower.
Publications: Dams in India.
Quote: “Civil engineering is the science of converting dreams of prosperity into the foundations of reality.”
4. Kanwar Sain (1899–1979)
Contribution: Director of Central Water and Power Commission, played a role in Indus Waters Treaty and irrigation strategy.
Publications: Reminiscences of an Engineer.
Quote: “Rivers can unite nations if engineers approach them with wisdom and fairness.”
5. K. L. Rao (1902–1986)

Contribution: Conceptualized the National Water Grid, led multiple irrigation projects.
Publications: India’s Water Wealth (1975).
Quote: “Water is wealth; the future of nations will depend on how wisely they use and share it.”
6. M. Ramachandran (1948– )

Contribution: Urban development expert, former Secretary of Ministry of Urban Development, key role in JNNURM mission.
Publications: Urban Renewal, Metro Rail Projects in India.
Quote: “Cities are engines of growth; their planning determines the quality of national development.”
7. Sudhir Krishna (1951– )
Contribution: Transport planning and Smart Cities Mission leader.
Publications: Multiple works on urban governance and infrastructure.
Quote: “Urban engineering is not about concrete alone; it is about making life livable.”
Why They Are Heroes
These civil engineers are not remembered merely for the structures they built, but for the nation they envisioned. Their projects:
Boosted agriculture and food security.
Connected isolated regions with modern infrastructure.
Improved urban life through sustainable planning.
Showed that engineering is not just about construction, but about transforming lives.
A Tribute to Civil Engineers
From dams and bridges to railways and tunnels, civil engineers have laid the foundation of India’s growth story. Their work is often unsung, but it silently powers the country every single day.
As we celebrate these real-life heroes, let us remember: civil engineering is not just a profession — it’s nation-building in its purest form.
Civil engineering is the invisible framework upon which society stands — roads, bridges, buildings, and water systems all begin with the calculations, designs, and integrity of civil engineers. But while concrete, steel, and stone can be measured, the ethical strength of the professionals behind the project is often less visible — and far more critical.
In recent years, India has seen several public infrastructure failures, cost overruns, and delays. Dig deeper, and a disturbing pattern emerges: compromised engineering ethics. This article explores how civil engineering ethics are not merely academic ideals, but the very foundation upon which public trust, safety, and progress depend.
Core Ethics in Civil EngineeringProfessional ethics in civil engineering are grounded in three pillars:
Public Safety Above All
Integrity in Design, Materials, and Execution
Responsibility Toward Environment and Future Generations
These aren’t just principles—they are legal, social, and professional obligations that every engineer assumes once they step into the field.
What Happens When Ethics Are Compromised Collapse of Structures, Collapse of TrustCase: In 2022, a bridge in Gujarat collapsed just days after being renovated. Investigations revealed that the renovation firm lacked structural engineering expertise, and the safety inspections were signed off without proper checks.
Ethical Breach: Certification without due diligence, failure to warn stakeholders, disregard for safety norms.
Use of Substandard MaterialsCivil engineers involved in procurement sometimes approve low-quality cement, steel, or aggregates in exchange for bribes or under pressure from contractors.
Example: A mid-size dam project in Maharashtra was found leaking within a year of commissioning — core samples revealed poor-grade concrete used to cut costs.
Ethical Breach: Misrepresentation, negligence, endangerment of public resources.
Tender Manipulation & FavoritismIt is increasingly common for tender specifications to be drafted in a way that favors a specific contractor or vendor — often due to internal collusion.
Example: An urban flyover project was delayed by 3 years due to legal disputes over irregularities in awarding tenders.
Ethical Breach: Conflict of interest, corruption, anti-competitive practices.
Forgery in Progress ReportsProject status reports are sometimes forged to claim stage payments without real progress on the ground, especially in government-funded rural projects.
Impact: Delayed roads, drainage systems, or schools in underserved areas — which exist only on paper.
Ethical Breach: Fraud, dereliction of duty, systemic dishonesty.
Wider Consequences of Ethical FailuresHuman Tragedies: Infrastructure collapse can directly cause injuries or fatalities.
Economic Drain: Rework, litigation, and emergency mitigation inflate costs and delay development.
Environmental Damage: Illegal dumping, deforestation, or over-extraction of materials often stems from unethical decision-making.
Public Distrust: Citizens lose faith in engineering institutions, contractors, and government schemes.
Global Reputation Hit: International investors hesitate to fund projects plagued with poor ethical records.
Increased Project Complexity: Smart cities, metros, high-speed rail — all require ethical engineers who can balance technology, safety, and public welfare.
PPP Model Expansion: With private players entering public infrastructure, transparency and ethical checks are essential to avoid profit-driven shortcuts.
Climate Crisis: Ethical decisions are now environmental decisions — engineers play a major role in ensuring sustainability.
Digital Oversight: With drone audits, satellite imagery, and real-time reporting, unethical practices are more likely to be exposed.
Ethics should be taught as core engineering coursework, with case studies of past failures and disasters.
Third-party audits should be mandatory at key project stages — not just at completion.
Engineers should be required to renew their license with mandatory ethics training every 3–5 years.
Civil engineers who report corruption must be given legal protection and anonymity.
E-tendering platforms with algorithmic review and open public access can reduce scope for manipulation.
Your role is more than just to design and construct — it is to serve society with honesty and foresight. The bridge you draw on CAD is not just a structure — it will carry mothers, workers, and schoolchildren. The foundation you calculate could hold a hospital or a school. You are not just shaping concrete — you are shaping lives.
The Future Demands Ethical FoundationsCivil engineering is one of the oldest and most noble professions — but only when its ethics are as strong as the structures it builds. As India scales up infrastructure, it must also scale up its ethical vigilance. Because without integrity, even the grandest projects are doomed to fall — in spirit, if not in structure.
1. Structural Design Consultancy
What It Is: Offering structural analysis and design services for residential and small commercial buildings.
Skills Needed: STAAD Pro, AutoCAD/Revit, knowledge of IS Codes, soil mechanics
Resources Required: A computer with licensed software, basic printer/scanner, professional license (if required)
Initial Budget: ₹1.5 – ₹2.5 Lakhs
Market Demand: Growing in Tier 2 and Tier 3 towns due to private home construction and local real estate.
Feasibility: High—can be started from home; no large team needed initially
Use Cases: Independent houses, small apartments, shops, town planning projects
Business Tips: Network with local contractors, panchayats, and architects
2. Land Surveying with Drones and GIS
What It Is: Providing topographic and layout surveys using drone technology and GIS mapping
Skills Needed: Drone piloting certification, GIS software (QGIS/ArcGIS), basic mapping knowledge
Resources Required: Survey-grade drone (DJI Phantom/RTK), GIS software, laptop
Initial Budget: ₹3 – ₹5 Lakhs (includes drone, licensing, training)
Market Demand: Landowners, real estate developers, municipal mapping projects
Feasibility: Moderate—requires some initial training and permissions
Use Cases: Land division, layout approvals, real estate plotting, road development
Business Tips: Get DGCA drone certification and work under an experienced mapper initially
3. Rainwater Harvesting and Groundwater Recharge Solutions
What It Is: Designing and installing rainwater harvesting systems for homes, schools, and colonies
Skills Needed: Plumbing design, basic hydrology, knowledge of water act and bylaws
Resources Required: Simple plumbing tools, rainwater filters, piping systems
Initial Budget: ₹50,000 – ₹1.5 Lakhs
Market Demand: High in water-scarce regions, government building mandates, NGOs
Feasibility: High—low investment and awareness-driven demand
Use Cases: Schools, residential complexes, panchayat buildings
Business Tips: Get IGBC/green certification and partner with local plumbers
4. Precast Concrete Elements Manufacturing
What It Is: Manufacturing pre-made concrete items like fencing poles, septic tanks, rings, pavers
Skills Needed: Knowledge of concrete mix design, casting, curing, and safety
Resources Required: Molds, small mixing unit, water tank, open space (1000+ sqft)
Initial Budget: ₹5 – ₹8 Lakhs
Market Demand: Steady in growing towns, especially for local construction
Feasibility: High—suitable for small-town demand; labor-intensive but profitable
Use Cases: Roads, housing, landscaping, public works
Business Tips: Supply to local contractors, municipal offices, and farms
5. Construction Material Testing Laboratory
What It Is: Providing testing for soil, concrete, bricks, and steel as per IS codes
Skills Needed: IS code compliance, material properties, lab equipment handling
Resources Required: Compression machine, sieves, slump cones, cube molds, space (250–500 sqft)
Initial Budget: ₹5 – ₹10 Lakhs (could start basic under ₹5 Lakhs)
Market Demand: Builders, government projects, NGOs, quality auditing firms
Feasibility: Medium—regulatory approval needed but offers consistent income
Use Cases: Real estate quality control, road projects, school buildings
Business Tips: Approach local PWD, contractors, and developers for tie-ups
6. Waterproofing and Soil Stabilization Contractor
What It Is: Offering services like chemical waterproofing, soil hardening, anti-termite treatment
Skills Needed: On-site application, chemistry of materials, vendor networking
Resources Required: Spray tools, safety gear, chemicals
Initial Budget: ₹1 – ₹3 Lakhs
Market Demand: New and old constructions, especially in monsoon-prone areas
Feasibility: Very high—skills are niche, margins are strong
Use Cases: Basement buildings, tanking structures, wet areas of homes
Business Tips: Learn from a senior contractor first, then scale independently
7. Road Repair and Maintenance Micro-Contractor
What It Is: Taking up small-scale road patchwork, paver-block laying, or footpath repair
Skills Needed: Road construction techniques, estimation, contractor licensing
Resources Required: Roller/rammers (rentable), tools, labor team
Initial Budget: ₹2 – ₹4 Lakhs
Market Demand: Panchayats, municipal bodies, private gated communities
Feasibility: Moderate—requires relationship building with civic authorities
Use Cases: Rural PMGSY roads, school compounds, approach roads
Business Tips: Bid on e-tenders; start as a subcontractor
8. Freelance Quantity Surveying and Estimation Services
What It Is: Preparing BOQs, costing, budgeting for small projects
Skills Needed: Costing software (CANDY, Excel, Buildsoft), IS codes
Resources Required: Laptop, software licenses, printer
Initial Budget: ₹50,000 – ₹1 Lakh
Market Demand: Architects, builders, small contractors
Feasibility: High—minimal capital and remote work friendly
Use Cases: Villas, low-rise apartments, interior renovations
Business Tips: Market on LinkedIn, Justdial, UrbanClap (now Urban Company)
Summary Table
Opportunity |
Budget Range (₹) |
Market Demand |
Feasibility |
Learning Curve |
Structural Design Consultancy |
1.5–2.5 Lakhs |
Medium–High |
High |
Moderate |
Drone Surveying |
3–5 Lakhs |
Growing |
Moderate |
High |
Rainwater Harvesting |
0.5–1.5 Lakhs |
High |
High |
Low–Moderate |
Precast Manufacturing |
5–8 Lakhs |
Stable |
High |
Moderate |
Testing Laboratory |
5–10 Lakhs |
Steady |
Medium |
High |
Waterproofing Services |
1–3 Lakhs |
Niche–Growing |
Very High |
Low–Moderate |
Road Maintenance |
2–4 Lakhs |
Local Government |
Moderate |
Moderate |
Quantity Surveying (Freelance) |
0.5–1 Lakh |
Digital–Flexible |
Very High |
Low |
What It Is: Offering structural analysis and design services for residential and small commercial buildings.
Skills Needed: STAAD Pro, AutoCAD/Revit, knowledge of IS Codes, soil mechanics
Resources Required: A computer with licensed software, basic printer/scanner, professional license (if required)
Initial Budget: ₹1.5 – ₹2.5 Lakhs
Market Demand: Growing in Tier 2 and Tier 3 towns due to private home construction and local real estate.
Feasibility: High—can be started from home; no large team needed initially
Use Cases: Independent houses, small apartments, shops, town planning projects
Business Tips: Network with local contractors, panchayats, and architects
What It Is: Providing topographic and layout surveys using drone technology and GIS mapping
Skills Needed: Drone piloting certification, GIS software (QGIS/ArcGIS), basic mapping knowledge
Resources Required: Survey-grade drone (DJI Phantom/RTK), GIS software, laptop
Initial Budget: ₹3 – ₹5 Lakhs (includes drone, licensing, training)
Market Demand: Landowners, real estate developers, municipal mapping projects
Feasibility: Moderate—requires some initial training and permissions
Use Cases: Land division, layout approvals, real estate plotting, road development
Business Tips: Get DGCA drone certification and work under an experienced mapper initially
What It Is: Designing and installing rainwater harvesting systems for homes, schools, and colonies
Skills Needed: Plumbing design, basic hydrology, knowledge of water act and bylaws
Resources Required: Simple plumbing tools, rainwater filters, piping systems
Initial Budget: ₹50,000 – ₹1.5 Lakhs
Market Demand: High in water-scarce regions, government building mandates, NGOs
Feasibility: High—low investment and awareness-driven demand
Use Cases: Schools, residential complexes, panchayat buildings
Business Tips: Get IGBC/green certification and partner with local plumbers
What It Is: Manufacturing pre-made concrete items like fencing poles, septic tanks, rings, pavers
Skills Needed: Knowledge of concrete mix design, casting, curing, and safety
Resources Required: Molds, small mixing unit, water tank, open space (1000+ sqft)
Initial Budget: ₹5 – ₹8 Lakhs
Market Demand: Steady in growing towns, especially for local construction
Feasibility: High—suitable for small-town demand; labor-intensive but profitable
Use Cases: Roads, housing, landscaping, public works
Business Tips: Supply to local contractors, municipal offices, and farms
What It Is: Providing testing for soil, concrete, bricks, and steel as per IS codes
Skills Needed: IS code compliance, material properties, lab equipment handling
Resources Required: Compression machine, sieves, slump cones, cube molds, space (250–500 sqft)
Initial Budget: ₹5 – ₹10 Lakhs (could start basic under ₹5 Lakhs)
Market Demand: Builders, government projects, NGOs, quality auditing firms
Feasibility: Medium—regulatory approval needed but offers consistent income
Use Cases: Real estate quality control, road projects, school buildings
Business Tips: Approach local PWD, contractors, and developers for tie-ups
What It Is: Offering services like chemical waterproofing, soil hardening, anti-termite treatment
Skills Needed: On-site application, chemistry of materials, vendor networking
Resources Required: Spray tools, safety gear, chemicals
Initial Budget: ₹1 – ₹3 Lakhs
Market Demand: New and old constructions, especially in monsoon-prone areas
Feasibility: Very high—skills are niche, margins are strong
Use Cases: Basement buildings, tanking structures, wet areas of homes
Business Tips: Learn from a senior contractor first, then scale independently
What It Is: Taking up small-scale road patchwork, paver-block laying, or footpath repair
Skills Needed: Road construction techniques, estimation, contractor licensing
Resources Required: Roller/rammers (rentable), tools, labor team
Initial Budget: ₹2 – ₹4 Lakhs
Market Demand: Panchayats, municipal bodies, private gated communities
Feasibility: Moderate—requires relationship building with civic authorities
Use Cases: Rural PMGSY roads, school compounds, approach roads
Business Tips: Bid on e-tenders; start as a subcontractor
What It Is: Preparing BOQs, costing, budgeting for small projects
Skills Needed: Costing software (CANDY, Excel, Buildsoft), IS codes
Resources Required: Laptop, software licenses, printer
Initial Budget: ₹50,000 – ₹1 Lakh
Market Demand: Architects, builders, small contractors
Feasibility: High—minimal capital and remote work friendly
Use Cases: Villas, low-rise apartments, interior renovations
Business Tips: Market on LinkedIn, Justdial, UrbanClap (now Urban Company)
| Structural Design Consultancy | 1.5–2.5 Lakhs | Medium–High | High | Moderate |
| Drone Surveying | 3–5 Lakhs | Growing | Moderate | High |
| Rainwater Harvesting | 0.5–1.5 Lakhs | High | High | Low–Moderate |
| Precast Manufacturing | 5–8 Lakhs | Stable | High | Moderate |
| Testing Laboratory | 5–10 Lakhs | Steady | Medium | High |
| Waterproofing Services | 1–3 Lakhs | Niche–Growing | Very High | Low–Moderate |
| Road Maintenance | 2–4 Lakhs | Local Government | Moderate | Moderate |
| Quantity Surveying (Freelance) | 0.5–1 Lakh | Digital–Flexible | Very High | Low |
Civil Engineering in India has been at the heart of national development for decades. With a growing population, rapid urbanization, and major government-led infrastructure initiatives, the field continues to offer substantial opportunities. However, shifts in technology, economic cycles, and policy directions have also led to evolving job roles and the obsolescence of some traditional functions. This report aims to highlight both the growth and decline areas within civil engineering and its subfields, the reasons behind these trends, and actionable pathways for graduates and professionals.
Growth Areas in Civil Engineering and Why They Are Rising
Infrastructure Development (Urban & Rural)
India is undergoing an infrastructure renaissance through government initiatives like Smart Cities Mission, Bharatmala, and PM Gati Shakti. These projects have generated massive demand for engineers in planning, structural design, and project management. From highways to rural roads and urban transit systems, civil engineers are central to execution and oversight.Sustainable Construction
With growing environmental awareness and tightening global climate policies, sustainable construction has emerged as a key focus area. Green buildings, LEED certifications, and the use of low-carbon materials have increased job roles for sustainability consultants, energy efficiency analysts, and eco-friendly design experts.Smart Infrastructure and IoT Integration
The integration of technology into infrastructure is becoming the norm. IoT-based solutions in traffic management, smart lighting, and waste disposal require civil engineers to collaborate with electronics and IT teams. This convergence creates roles like Civil-IoT Integration Engineers and Infrastructure Technologists.Building Information Modeling (BIM)
BIM adoption is growing rapidly due to its ability to reduce project delays and enhance visualization. International firms and domestic EPC contractors are increasingly using BIM for real-time planning, costing, and design. Expertise in tools like Revit, Navisworks, and Civil 3D is a major asset.Urban Mobility Projects
Rising urban populations are putting stress on transportation networks. Projects like metro rail, expressways, BRT corridors, and pedestrian-friendly infrastructure are expanding. This growth demands skilled transport engineers, geotechnical specialists, and urban planners.Disaster-Resilient Structures
India's vulnerability to earthquakes, floods, and other climate events has led to a focus on disaster-resilient designs. Civil engineers trained in structural dynamics, seismic codes, and resilient architecture are in high demand, especially in sensitive zones.
Declining Areas in Civil Engineering and Reasons for the Downturn
Manual Site Supervision
As technology advances, traditional manual supervision is being replaced by automated tools like drones, CCTV, and real-time project tracking apps. These allow for better monitoring, reduced human error, and fewer site-level staffing needs.Low-End Real Estate Construction
The affordable housing sector, while initially booming, is slowing down due to oversupply, lower consumer purchasing power, and policy bottlenecks. This has led to reduced employment for site engineers and junior construction supervisors in this niche.Conventional Drafting Roles
Engineers solely proficient in 2D AutoCAD are finding it difficult to remain relevant. With the shift towards 3D design and BIM, basic drafting roles are being replaced by multidisciplinary modeling jobs requiring advanced software proficiency.Government Contractor Roles
Government civil works often suffer from inconsistent funding, delayed payments, and bureaucratic inefficiencies. Many graduates are opting out of these unstable career paths, and private players are taking over infrastructure delivery through Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs).Bridge & Dam Engineering in PSUs
While previously considered prestigious, roles in bridge and dam engineering within public sector undertakings (PSUs) are declining. This is due to a lack of new large-scale projects, increased reliance on consultants, and overall PSU hiring freezes or contractual staffing models.
The future of civil engineering in India is promising, provided professionals adapt to the demands of a modern, technology-integrated, and sustainability-driven infrastructure environment. Traditional roles are declining, but dynamic engineers who embrace innovation will find ample opportunities both in employment and entrepreneurship.
Engineering Job Market: Growth & Decline Areas
1. Mechanical Engineering
Growth Areas:
- CNC Machining & 3D Printing: High demand for precision manufacturing in automobile, aerospace, and medical device industries.
- Renewable Energy (HVAC, Solar, Wind Turbines): Companies need mechanical engineers for solar panel mounting, wind turbine designs, and energy-efficient HVAC systems.
Decline Areas:
Traditional Manufacturing & Auto Parts Production:
Due to automation & AI-driven robots, jobs in basic machining, manual assembly lines, and conventional welding are shrinking.
Electric Vehicles (EVs) require fewer mechanical parts compared to fuel-based vehicles, reducing demand for engine and transmission-related jobs.
2. Electrical Engineering
Growth Areas:
- Solar Power & EV Infrastructure: High demand for solar panel installation, battery storage technology, and EV charging stations.
- Industrial & Home Automation: Smart grids, IoT-based industrial automation, and smart homes need skilled electrical engineers.
- Power Electronics & Renewable Energy Systems: The shift to clean energy is creating opportunities in inverters, power converters, and smart grids.
Decline Areas:
Conventional Power Plants (Coal & Thermal):
India is reducing coal dependence and shifting to renewables, decreasing jobs in traditional thermal power plants.
Many state-run electricity boards are reducing hiring as they focus more on automation & efficiency improvements.
3. Civil Engineering
Growth Areas:
- Green & Smart Infrastructure: High demand for sustainable, eco-friendly building designs.
- Urban Development & Smart Cities: Government initiatives like Smart Cities Mission are driving demand for urban planning & metro projects.
- Prefabrication & Modular Construction: Pre-fab buildings reduce construction costs and time, creating new job opportunities.
Decline Areas:
Traditional Road & Bridge Construction Jobs:
- Automation & AI are replacing traditional surveying, site inspection, and blueprint designing roles.
- Government spending on new highways is reducing in some regions due to budget constraints.
4. Chemical Engineering
Growth Areas:
- Pharmaceuticals & Biotech: The rise of biotech startups, vaccine production, and drug research is boosting demand for chemical engineers.
- Waste Treatment & Environmental Engineering: Industrial pollution control, water treatment plants, and chemical recycling are growing sectors.
- Green Chemicals & Biofuels: India is investing in bioethanol, hydrogen fuels, and biodegradable plastics.
Decline Areas:
Traditional Petrochemical & Oil Refining Jobs:
- As renewable energy adoption increases, demand for petroleum-based products is declining.
- Many oil refineries are cutting workforce sizes due to automation and efficiency improvements.
5. Aerospace & Automobile Engineering
Growth Areas:
- Electric Aircraft & UAVs (Drones): The global push for electric-powered aircraft and cargo drones is driving demand for aeronautical engineers.
- Autonomous Vehicles & AI in Automobiles: Self-driving car technology and AI-based vehicle design optimization are emerging fields.
- Space Technology & Satellites: With ISRO and private space startups (Skyroot, Agnikul Cosmos), space engineering jobs are expanding.
Decline Areas:
Traditional Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Manufacturing:
- As EVs replace fuel-based cars, jobs in traditional car engine manufacturing are shrinking.
- Companies like Maruti, Tata, and Mahindra are shifting focus to electric and hybrid vehicles, leading to reduced hiring in traditional automobile plants.
Engineering Field: Growth Areas & Declining Areas Summary in Table format.
| Mechanical | CNC, 3D Printing, EV Components | Traditional Auto Parts, IC Engines |
| Electrical | Solar, EV Charging, Smart Grids | Coal Power Plants, Traditional Power Distribution |
| Civil | Smart Cities, Green Buildings | Traditional Roads & Bridges |
| Chemical | Biotech, Waste Treatment, Green Chemicals | Petroleum, Traditional Plastics |
| Aerospace | Drones, Space Tech, AI in Automobiles | IC Engine Vehicles, Manual Aircraft Manufacturing |
Current Demand and Projected Growth Rate in India:
The civil engineering market in India is experiencing significant expansion, with a robust projected Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2024 to 2030, anticipating a substantial market size of US$ 801.610 million by 2030 [1]. This growth is underpinned by the continuous development of infrastructure across the country. The demand for civil engineers in India is also projected to grow at a strong rate of 9% annually between 2018 and 2028, driven by the persistent need for infrastructure development [2]. Some sources even suggest a higher annual growth rate of 25% in the field, emphasizing the increasing demand for both infrastructure and qualified professionals to realize these projects [3]. Furthermore, India is projected to need over 4 million civil engineers in the next decade, highlighting the vast scale of the demand within this sector [4]. The consistent growth projections and the sheer number of professionals required indicate a healthy and expanding job market for civil engineers in India, with considerable long-term potential.
Key Industries Actively Hiring in India:
Civil engineers in India find employment opportunities across a broad spectrum of industries. Key among these are the Civil Services, which offer stable government positions; Private Firms involved in the construction of residential and commercial buildings, roads, bridges, and dams; the Indian Armed Forces, where civil engineers play a crucial role in planning and construction projects; and Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs) that undertake large-scale public welfare projects [4]. Specific examples of major PSUs that actively recruit civil engineers include Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL), Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL), Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), Oil and Natural Gas Corporation Limited (ONGC), and Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL) [2]. This diverse hiring landscape, encompassing both the stability of the government sector and the dynamism of private construction, demonstrates a robust and multifaceted job market for civil engineers in India, with a strong focus on national infrastructure development.
Impact of Emerging Technologies:
The field of civil engineering is undergoing a significant transformation due to the emergence of new technologies. These include the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) in infrastructure monitoring, allowing for real-time data collection and analysis; Artificial Intelligence (AI)-powered predictive maintenance, enabling proactive identification and resolution of potential issues; the use of digital twins for virtual construction planning, improving risk management and project simulation; construction automation, including the use of robots and self-driving vehicles to enhance efficiency and safety; the application of 3D printing for creating structures and components; the use of drone technology for site surveying and progress monitoring; advancements in Building Information Modeling (BIM) for enhanced collaboration and data integration; a growing emphasis on green building design and sustainable construction practices; and the adoption of modular and prefabricated construction methods for faster and more efficient building [5]. These emerging technologies are revolutionizing civil engineering practices, leading to smarter, more sustainable, and digitally integrated construction, which in turn demands engineers equipped with new and evolving skill sets.
Specific Skills and Specializations in High Demand in India:
The demand for specific skills and specializations within civil engineering in India is evolving to reflect the impact of emerging technologies and the changing needs of the industry. There is an increasing demand for skills related to sustainable and green construction practices, the development and management of smart cities and infrastructure, techniques for prefabrication and modular construction, the application of AI and Machine Learning in construction planning and analysis, knowledge of advanced construction materials such as geopolymer and self-healing concrete, expertise in 3D printing for construction applications, proficiency in transportation and high-speed rail development, understanding of blockchain technology for construction management, the ability to design disaster-resilient infrastructure, and knowledge of waste management and circular economy principles in construction [4]. Additionally, expertise in BIM and digital modeling software, the operation and analysis of data from automation control systems and drones, and the implementation of sustainable design principles and modular construction techniques are becoming increasingly valuable [5]. This shift in demand clearly indicates a move towards specializations that focus on sustainability, smart infrastructure solutions, digitally integrated construction technologies, and the utilization of advanced materials, reflecting the modernization of the industry.
Typical Salary Ranges (Entry-Level, Mid-Level, Experienced) in India:
Salary ranges for civil engineers in India can vary considerably depending on the specific job role, the level of experience, the industry of employment (government sector versus private firms), and the complexity and scale of the projects involved. For instance, a Construction Manager might earn around 13 LPA (Lakhs Per Annum), while a Design Manager could expect about 5.78 LPA, and a CAD Technician around 5.38 LPA. Field Service Engineers may start at a lower range of 2.55 LPA, whereas experienced Engineering Project Managers could command salaries as high as 16.25 LPA, and Consulting Engineers around 12 LPA [4]. The general average salary range for civil engineers in India starts from approximately INR 3.6 lakhs to 7 lakhs and can go higher per annum [3]. Specific roles like Building Managers might earn around 6.75 LPA, Fire Managers about 8.12 LPA, and Planning Engineers roughly 6 LPA [4]. This diversity in salary figures across different roles highlights the importance of specialization and the potential for significant earning growth with increased experience and the acquisition of in-demand skills within the civil engineering domain.
Executive Summary:
The Indian engineering job market in 2025 is characterized by significant dynamism, primarily fueled by rapid technological advancements and sustained economic growth. This report provides a comparative analysis of the job market trends for five mainstream engineering branches in India: Civil Engineering, Electrical Engineering, Computer Engineering, Chemical Engineering, and Mechanical Engineering. The purpose of this analysis is to offer strategic insights for professionals navigating this evolving landscape. Key findings indicate that Computer Engineering currently exhibits the strongest growth and demand, largely due to the ongoing digital transformation across industries. Mechanical Engineering also presents substantial opportunities owing to its foundational role in a wide array of sectors. While Civil, Electrical, and Chemical Engineering demonstrate steady growth and demand within their respective domains, the impact of emerging technologies is a critical factor influencing the trajectory of all five branches. The strongest trends are observed in Computer Engineering, driven by the digital revolution, and in Mechanical Engineering, supported by its adaptability across diverse sectors. These trends are primarily attributed to rapid technological advancements in areas like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and automation, coupled with government initiatives such as Make in India and Skill India, and consistent industrial expansion.
Introduction:
The Indian economy is currently experiencing a phase of rapid expansion, with an increasing emphasis on technological advancement and infrastructure development, which has a direct and significant impact on the engineering sector. Engineering serves as a fundamental pillar of India's progress, driving innovation, the expansion of essential infrastructure, and overall technological progress. This report will focus on five mainstream engineering branches that are crucial to this development: Civil Engineering, which deals with infrastructure and construction; Electrical Engineering, concerned with power and electronics; Computer Engineering, specializing in software and information technology; Chemical Engineering, focused on processes and materials; and Mechanical Engineering, which encompasses design and manufacturing. The primary objective of this report is to provide a comprehensive and data-driven comparative analysis of the job market trends for these five engineering branches within India for the year 2025 and the near future. This analysis aims to equip professionals with the necessary insights to make informed decisions regarding their career paths. The report will cover key aspects for each branch, including the current level of demand, the projected growth rate, the primary industries that are actively hiring, the influence of emerging technologies, the specific skills and specializations that are in high demand, and the typical salary ranges for professionals at different stages of their careers. The information presented in this analysis is derived from a variety of recent industry reports, surveys conducted by job portals and educational institutions, and relevant government statistics
Comparative Analysis of Job Market Trends:
- Demand:
Currently, Computer Engineering and Mechanical Engineering exhibit the highest demand in India in 2025. The demand for Computer Engineering is significantly boosted by the thriving IT sector and the ongoing digital transformation across various industries, with over 82,000 job openings reported 14. Mechanical Engineering also experiences strong demand due to its fundamental role in a wide array of industries, particularly manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace 23. Civil Engineering demonstrates robust demand driven by extensive infrastructure projects 2, while Electrical and Chemical Engineering maintain steady demand across their respective sectors 6. The sheer volume of job openings in Computer Engineering suggests a quantitatively higher current demand compared to the more general descriptions of demand in other engineering fields.
- Projected Growth Rate:
Computer Engineering is projected to have the most significant growth rate in the near future, with an anticipated 22% increase in tech jobs 11and a 21.4% CAGR in the engineering software market 13. Civil Engineering also shows strong growth projections, with a CAGR of 7.8% for the market 1and an annual demand growth of 9% for professionals 2, with some estimates going as high as 25% annually 3. Electrical Engineering is expected to grow at around 5% annually in terms of employment 8, with a notable 12% projected annual growth in the electrical equipment manufacturing market 6. Mechanical Engineering's growth is projected to be in the range of 4-7% 24, while Chemical Engineering is expected to see an approximate annual growth of 8% in demand 19. The consistently higher growth rate projected for Computer Engineering indicates that it will likely continue to generate more new job opportunities compared to the other branches in the coming years.
Key Industries:The primary industries actively hiring professionals vary across the engineering branches. Computer Engineering is heavily concentrated in the IT services sector, software development companies, and the e-commerce industry. Mechanical Engineering has the broadest distribution, with significant hiring in manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and the energy sector. Civil Engineering is primarily focused on infrastructure and construction projects, with substantial involvement from the government sector. Electrical Engineering sees major hiring in power generation, telecommunications, and the automation industry. Chemical Engineering is vital for the chemical manufacturing and processing industries, including pharmaceuticals and the energy sector. The concentration of Computer Engineering in the rapidly expanding technology sector contrasts with the wider distribution of the other branches, suggesting different sensitivities to sector-specific economic fluctuations.
- Engineering Branch and Their Key Hiring Industries
Civil:-
Civil Services, Private Construction Firms, Indian Armed Forces, Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs), Infrastructure Development Companies
Electrical:-
Power Generation, Telecommunications, Automation & Robotics, Semiconductors, Renewable Energy, Electrical Equipment Manufacturing, Electronics Manufacturing
Computer:-
IT Services, Software Development, E-commerce, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Companies, Product Development Companies, Cybersecurity Firms
Chemical:-
Oil & Gas, Chemical Manufacturing, Pharmaceuticals, Food Processing, Biotechnology, Petroleum, Fertilizer, Power and Energy, Water Treatment, FMCG, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration
Mechanical:-
Manufacturing, Automotive, Aerospace, Energy, Construction, Healthcare, Electronics, Pharmaceuticals, Heavy Machinery, Power Generation, Chemical Processing, Food and Beverage, Metals, Industrial Equipment, Machinery Manufacturing, Automation Systems, Consulting, Project Management
- Required Skills: While core engineering principles remain fundamental, all five branches increasingly demand digital literacy and skills related to emerging technologies. Computer Engineering professionals are expected to possess strong programming skills, expertise in cloud computing platforms, and knowledge of AI and ML tools. Mechanical Engineering requires proficiency in CAD software, understanding of automation and robotics, and knowledge of sustainable design principles. Civil Engineering professionals need skills in BIM software, knowledge of smart infrastructure technologies, and an understanding of sustainable construction practices. Electrical Engineering demands expertise in renewable energy systems, smart grid technologies, and embedded systems design. Chemical Engineering is focusing on skills related to process optimization, sustainable chemical processes, and biotechnology applications. This common need for digital skills across all engineering disciplines highlights a fundamental shift in the profession, where traditional domain expertise must be complemented by technological proficiency.
- Salary Expectations: In terms of salary expectations, Computer Engineering generally offers the highest compensation, particularly at the entry and mid-levels, owing to the intense demand within the rapidly expanding IT sector. Entry-level salaries in Computer Engineering can reach up to 11.8 LPA 11, and mid-level professionals often earn in excess of 10 LPA 14. Mechanical and Chemical Engineering also provide competitive salary packages, especially for mid-level and experienced professionals, with potential earnings reaching up to 12 LPA and 20+ LPA, respectively 21. Civil and Electrical Engineering offer good salary prospects as well, with entry-level positions ranging from 3-6 LPA and 4-6 LPA, respectively 8, and opportunities for higher earnings with specialization and increased experience. The salary premium observed in Computer Engineering reflects the intense competition for skilled talent within the rapidly growing technology industry in India.
- Typical Salary Ranges (LPA) by Engineering Branch and Experience Level
Civil:-
Entry Level ( 0-3 Years of Enperience):- 3.6 - 5.0
Mid Level( 3-7 Years of Enperience):- 5.0 - 7.5
Highly Experience Level ( 7+ Years of Experience):- 7.5 - 15 +
Electrical:-
Entry Level ( 0-3 Years of Enperience):- 3.0 - 4.5
Mid Level( 3-7 Years of Enperience):- 4.5 - 9.0
Highly Experience Level ( 7+ Years of Experience):-8.0 - 12+
Computer:-
Entry Level ( 0-3 Years of Enperience):- 6.0 - 11.8
Mid Level( 3-7 Years of Enperience):- 8.0 - 15.0
Highly Experience Level ( 7+ Years of Experience):-12.0 - 25+
Chemical:-
Entry Level ( 0-3 Years of Enperience):- 3.0 - 8.0
Mid Level( 3-7 Years of Enperience):- 5.0 - 10.0
Highly Experience Level ( 7+ Years of Experience):- 8.0 - 20+
Mechanical:-
Entry Level ( 0-3 Years of Enperience):- 3.0 - 6.0
Mid Level( 3-7 Years of Enperience):- 6.0 - 12.0
Highly Experience Level ( 7+ Years of Experience):- 12.0 - 20+
Comparative Analysis of Job Market Trends Across Mainstream Engineering Fields
1. Introduction
The engineering job market has undergone significant changes over the last five years, influenced by technological advancements, industry demand, and regional economic factors. This report provides a comparative analysis of job trends across key engineering disciplines globally and in India, backed by industry reports and expert analysis.
2. Overview of Engineering Fields Considered
Mechanical Engineering
Civil Engineering
Electrical Engineering
Electronics Engineering
Computer Science & Software Engineering
Chemical Engineering
Aerospace Engineering
3. Job Growth Trends (2019-2024)
Engineering FieldGlobal Job Growth (%)India Job Growth (%)Key Drivers
Mechanical +5% +6% Automation, Robotics, Renewable Energy (Source: World Economic Forum, Engineering Workforce Report 2023) Civil +3% +4% Urbanization, Smart Cities, Infrastructure Development (Source: India Infrastructure Report 2023) Electrical +4% +5% Power Grids, Renewable Energy, Electric Vehicles (EVs) (Source: International Energy Agency, Global Energy Outlook 2024) Electronics +2% +3% Consumer Electronics, Semiconductor Industry (Source: Semiconductor Industry Association 2023) Computer Science +12% +15% AI, Cloud Computing, Cybersecurity, Software Development (Source: Gartner IT Jobs Report 2024) Chemical +1% +2% Sustainable Materials, Green Chemistry, Pharmaceuticals (Source: Global Chemical Industry Report 2023) Aerospace +6% +7% Space Exploration, Defense, Private Aviation Growth (Source: NASA & ISRO Employment Reports 2023) 4. Key Findings & Comparative Analysis 4.1 Computer Science & Software Engineering
Highest Growth Rate due to demand in AI, ML, cybersecurity, and cloud technologies. (Source: McKinsey Digital Workforce Report 2024)
Remote Work Flexibility allows companies to hire globally, increasing competition.
India as an IT Hub has significantly contributed to its rapid job market expansion. (Source: NASSCOM India IT Jobs Report 2023)
4.2 Mechanical, Electrical, and Civil Engineering
Steady Growth but not as exponential as software fields. (Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics, Engineering Job Outlook 2024)
Automation & AI Integration is reshaping traditional roles.
Renewable Energy & EVs boosting opportunities in Electrical and Mechanical fields.
Smart Cities & Infrastructure Growth supporting Civil Engineering job demand. (Source: World Bank Infrastructure Investment Report 2023)
4.3 Electronics & Chemical Engineering
Slower Growth due to automation reducing manual design and manufacturing roles.
Semiconductor Industry Boom creating niche opportunities in Electronics. (Source: Semiconductor Industry Association 2023)
Sustainability Focus in Chemical Engineering opening new doors in green chemistry. (Source: Global Chemical Engineering Outlook 2024)
4.4 Aerospace Engineering
Stable to Growing Market with increased investments in private space exploration (SpaceX, ISRO, Blue Origin, etc.).
Defense & Commercial Aviation driving demand. (Source: Boeing & Airbus Industry Reports 2023)
5. Future Prospects & Emerging Trends
Interdisciplinary Skills: Engineers combining traditional skills with AI, IoT, and robotics will have a competitive edge. (Source: Harvard Business Review 2024)
Sustainability & Green Engineering: High demand in renewable energy, electric vehicles, and waste management.
Space & Defense Sector Expansion: Increasing aerospace engineering opportunities.
Upskilling & Reskilling: Engineers must adapt to digital transformations to remain relevant. (Source: LinkedIn Workforce Report 2023)
6. Conclusion
While Computer Science & Software Engineering leads in job market expansion, other engineering fields remain essential, with opportunities evolving due to technological shifts. Engineers who integrate software, automation, and sustainability into their expertise will have higher employability in the future.
Sources & References:
World Economic Forum, Engineering Workforce Report 2023
Bureau of Labor Statistics, Engineering Job Outlook 2024
NASSCOM India IT Jobs Report 2023
McKinsey Digital Workforce Report 2024
Semiconductor Industry Association 2023
Global Chemical Industry Report 2023
India Infrastructure Report 2023
International Energy Agency, Global Energy Outlook 2024
Boeing & Airbus Industry Reports 2023
NASA & ISRO Employment Reports 2023
Harvard Business Review 2024
LinkedIn Workforce Report 2023
This report provides a structured comparison of engineering job markets. Let me know if you need more detailed insights or additional data points!

Civil engineering is one of the oldest and most important branches of engineering. As such, it also plays a central role in shaping modern society through the design and construction of its infrastructure. From roads to bridges to skyscrapers and dams, civil engineers help design and oversee nearly all aspects of everyday life. The following is a guide to what civil engineering is, important subjects, career scope, and best colleges in India if you are looking to pursue a career path in civil engineering.
And that is what Engineer's Heaven is all about, bringing you the best resources to become a successful engineer. Whatever help you need, whether it be course information you seek, exam preparation tips or career guidance, we are here to provide assistance!
What is Civil Engineering?
Civil engineering deals with the design, construction and maintenance of physical and natural built environments. These projects include highways, railways, airports, tunnels and sewage systems. Make sure these structures are safe, durable and sustainable. Their efforts have a direct impact on the economy, urban development, and public welfare.
The Civil Engineering Courses combines creativity, problem solving, and technical know-how. It involves extensive knowledge of materials, environmental considerations, and construction methodologies. Do what you love — if you love to build and solve real life problems, civil engineering may be exactly what you want.
Subjects in Civil Engineering
The technical and subject-oriented aspect of study are taught on many subjects in a bachelor of civil engineering degree. The civil engineering subjects include:
- Structural Engineering
This major deals with the designing of buildings, bridges and other structures. Engineers learn to make things stable and strong and safe.
- Geotechnical Engineering
It is concerned with soil mechanics and foundation design. Engineers study soil properties in order to build sound structures and infrastructure.
- Transportation Engineering
This topic includes the design and layout of roads, railways, and airports. It aids in making transportation more safe and efficient.
- Environmental Engineering
It deals with waste management and pollution control, water treatment. Urban areas evolve, engineers trying to design something eco-friendly around it.
- Construction Management
This topic covers project planning, cost estimation, and resource management. Many engineers are taught to deliver projects on time and within budget.
- Hydraulics Engineering & Water Resources
This includes creating dams, canals and irrigation systems. Fluid mechanics is studied by engineers to control water resources.
In addition to core subjects, students take surveying, material science, and computer-aided design (CAD). This prepares graduates to be effective at tackling real world engineering.
Civil Engineering Career / Job Options
There are great career prospects for civil engineers, whether in the public or private sector. As urbanization accelerates and infrastructure evolves, there is an increasing need for qualified professionals. Here are a few popular career choices:
Civil Engineers in Government Sector: Numerous civil engineers get hired as government engineers for authorities such as PWD, NHAI, municipal corporations, etc. They manage public infrastructure projects.
- Structural Engineer : Designs and analyzes structures to ensure they are safe and durable.
- Construction management: They manage teams, budgets, and timelines for a construction project
- Transportation Engineer: These professionals design and optimize road networks, analyze traffic flow, and manage public transit systems.
- Environmental Engineer: A professional who specializes in environmental protection technology, pollution control, and waste management systems.
They can also work in contractor organisations, consultancy farm and research establishment. We usually start our own business like construction or design services.
Top Civil Engineering Colleges in India
Construction of future is directly linked to the college you select for Engineering. Few of the best civil engineering colleges are in the country:
- Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs)
Ranked at 1: IIT Bombay, IIT Delhi, IIT Madras, IIT Kharagpur These institutes provide high standard education with appropriate research.
- All the National Institutes of Technology (NITs)
Striking the right chord among the NITs like NIT Trichy, NIT Warangal, NIT Surathkal have gained tremendous recognition for their academic excellence and placement records.
- Birla Institute of Technology and Science (BITS) Pilani
It has very good infrastructure and industry exposure. Its flexible curriculum allows students to delve into different fields.
- Delhi Technological University (DTU)
It is renowned for its excellent civil engineering department and collaborations with industries.
- VIT (Vellore Institute of Technology)
VIT provides state-of-the-art facilities, seasoned faculty, and excellent placement prospects.
This list includes some of the best colleges that offer excellent education and training to help students excel in their careers in civil engineering.
Why Choose Civil Engineering?
Civil engineering is one of the most exciting and rewarding domains. You’re able to build things that last and give back to society. Below are a few reasons to pursue this profession:
- Increased Demand: Infrastructure development is essential across the world, which means job security.
- Variety of Roles: Civil engineers serve in an array of industries, including construction, environmental management, and more.
- Creativity & Innovation: Engineers create original solutions for real-world problems.
- Good Salary Packages: The salaries and perks for civil engineers are quite good and with experience, they are offered great packages.
There is a blooming scope of civil engineering nowadays. It combines technical expertise, creativity, and problem-solving ability. This is for you if you care about building the future!
Engineers Heaven, if you are seeking help, niche or resources's knowledge. We help students grow successful careers with expert advice and Insights. Want to know more, Sign up with us and start your knowledge Civil engineering journey today!
(Disclaimer: This statistics could be different in different part of World and Different timeline. this statistics has been generated based on data available till 2025 or relavant time span.)